Textbook Question
Draw the condensed structural formulas for the products of the reaction of aspartate and α-ketoglutarate which is catalyzed by aspartate transaminase (AST).

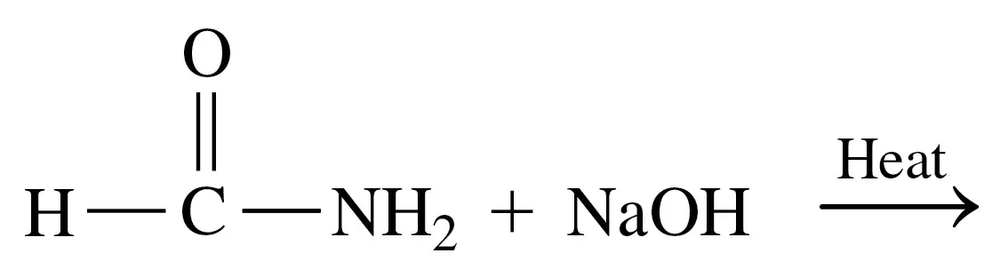
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

Draw the condensed structural formulas for the products of the reaction of aspartate and α-ketoglutarate which is catalyzed by aspartate transaminase (AST).
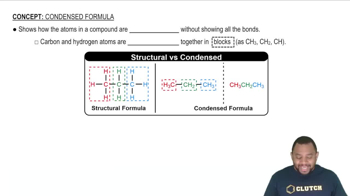
Write the IUPAC name for each of the following:
b .
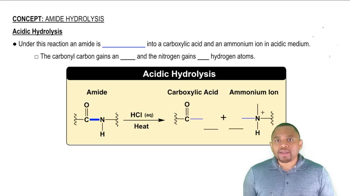
Draw the condensed structural or line-angle formulas for the products from the hydrolysis of each of the following:
a.
Draw the condensed structural or line-angle formulas for the products from the hydrolysis of each of the following:
b.
Draw the line-angle formula and write the IUPAC name for each of the following:
a. A carboxylic acid that has the formula C6H12O2, with no substituents
Propyl acetate is the ester that gives the odor and smell of pears.
<IMAGE>
a. Draw the condensed structural formula for propyl acetate.