Draw the condensed structural or line-angle formulas for the products from the hydrolysis of each of the following:
b.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
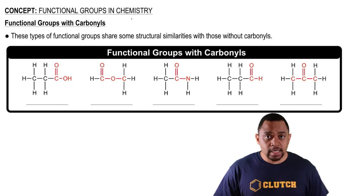
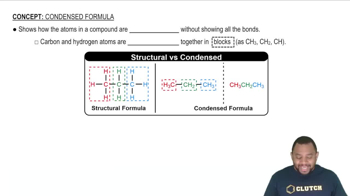
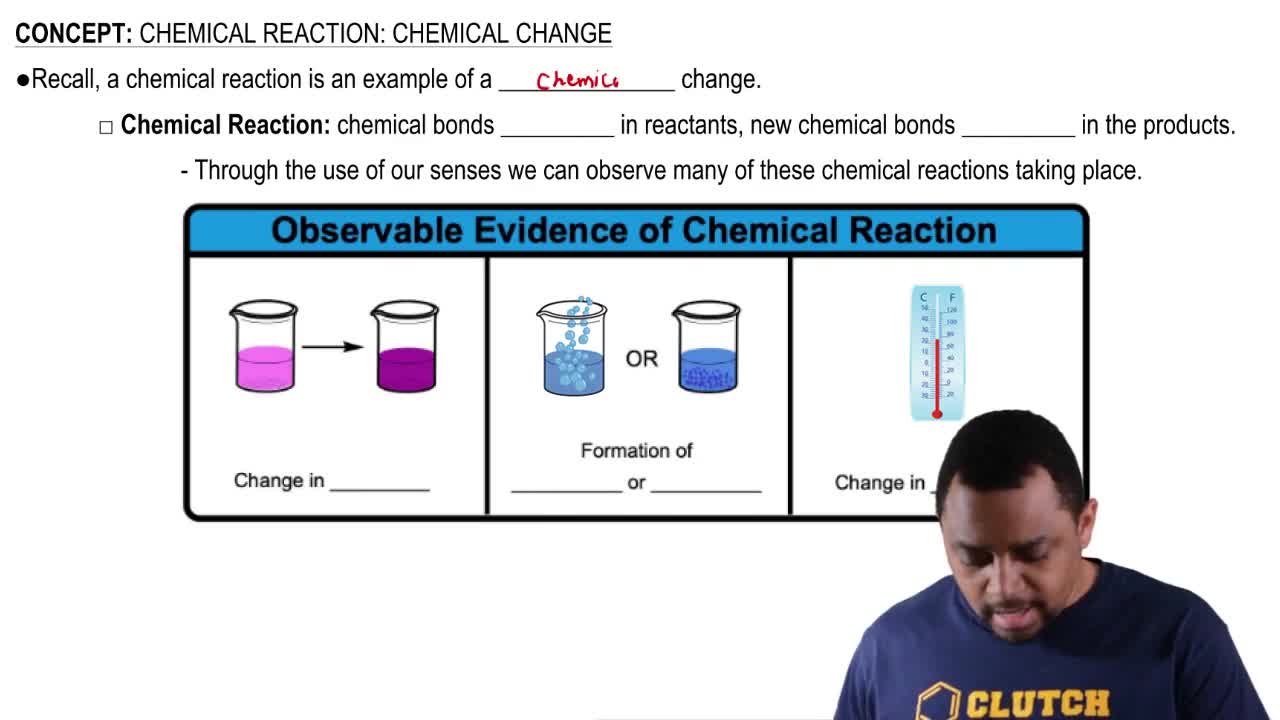
Draw the condensed structural or line-angle formulas for the products from the hydrolysis of each of the following:
b.
Draw the condensed structural or line-angle formulas for the products from the hydrolysis of each of the following:
b.
Draw the line-angle formula and write the IUPAC name for each of the following:
a. A carboxylic acid that has the formula C6H12O2, with no substituents
Propyl acetate is the ester that gives the odor and smell of pears.
b. Use condensed structural formulas to write the balanced chemical equation for the formation of propyl acetate.
Propyl acetate is the ester that gives the odor and smell of pears.
d. Use condensed structural formulas to write the balanced chemical equation for the base hydrolysis of propyl acetate with NaOH.
Propyl acetate is the ester that gives the odor and smell of pears.
<IMAGE>
e. How many milliliters of a 0.208 M NaOH solution is needed to completely hydrolyze (saponify) 1.58 g of propyl acetate?