Back
BackProblem 17
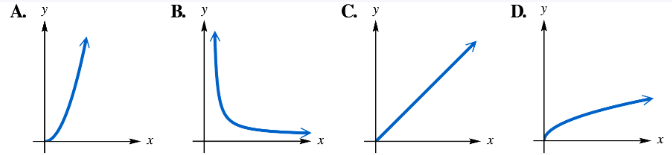
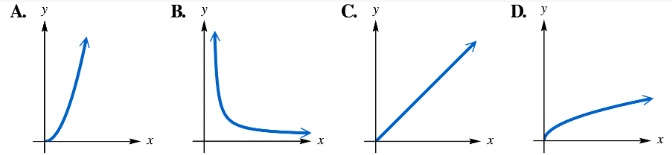
Match each statement with its corresponding graph in choices A–D. In each case, k > 0. y varies directly as x. (y=kx)
Problem 17
Use the factor theorem and synthetic division to determine whether the second polynomial is a factor of the first. x3+2x2+3; x-1
Problem 17
Solve each quadratic inequality. Give the solution set in interval notation. x2 + x - 30 ≤ 0
Problem 17
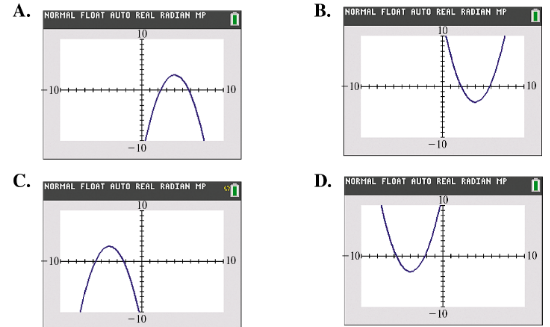
Match each function with its graph without actually entering it into a calculator. Then, after completing the exercises, check the answers with a calculator. Use the standard viewing window. ƒ(x) = (x + 4)2 - 3
Problem 17
Use synthetic division to perform each division.
Problem 18
Graph each function. Determine the largest open intervals of the domain over which each function is (a) increasing or (b) decreasing. ƒ(x)=(1/3)(x+3)4-3
Problem 18
Use synthetic division to find ƒ(2). ƒ(x)=x5+4x2-2x-4
Problem 18
Use the factor theorem and synthetic division to determine whether the second polynomial is a factor of the first. 2x3+x+2; x+1
Problem 19
Graph each function. Determine the largest open intervals of the domain over which each function is (a) increasing or (b) decreasing. ƒ(x)=(1/2)(x-2)2+4
Problem 19
Match each statement with its corresponding graph in choices A–D. In each case, k > 0. y varies directly as the second power of x. (y=kx2)
Problem 19
Use the factor theorem and synthetic division to determine whether the second polynomial is a factor of the first.
Problem 19
Graph the following on the same coordinate system.
(a) y = x2
(b) y = 3x2
(c) y = 1/3x2
(d) How does the coefficient of x2 affect the shape of the graph?
Problem 19
Solve each quadratic inequality. Give the solution set in interval notation. x2 - 2 > x
Problem 19
Use synthetic division to perform each division. (x4 - 3x3 - 4x2 + 12x) / x-2
Problem 20
Use the factor theorem and synthetic division to determine whether the second polynomial is a factor of the first. See Example 1.
Problem 21
Write each formula as an English phrase using the word varies or proportional. C=2πr, where C is the circumference of a circle of radius r.
Problem 21
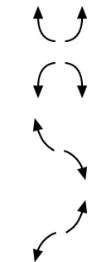
Use an end behavior diagram, as shown below, to describe the end behavior of the graph of each polynomial function. ƒ(x)=5x5+2x3-3x+4
Problem 21
Use synthetic division to perform each division. (x3 - 1) / (x-1)
Problem 21
Graph the following on the same coordinate system.
(a) y = (x - 2)2
(b) y = (x + 1)2
(c) y = (x + 3)2
(d) How do these graphs differ from the graph of y = x2?
Problem 21
If ƒ(x) is a polynomial function with real coefficients, and if 7+2i is a zero of the function, then what other complex number must also be a zero?
Problem 21
Solve each quadratic inequality. Give the solution set in interval notation. 2x2 + 5 ≤ 11x
Problem 22
Use an end behavior diagram, as shown below, to describe the end behavior of the graph of each polynomial function. ƒ(x)=-x3-4x2+2x-1
Problem 22
Use synthetic division to perform each division. x4-1 / x-1
Problem 22
Factor ƒ(x) into linear factors given that k is a zero.
Problem 23
Use one of the end behavior diagrams below, to describe the end behavior of the graph of each polynomial function.
Problem 23
Write each formula as an English phrase using the word varies or proportional. r = d/t, where r is the speed when traveling d miles in t hours.
Problem 23
Graph each quadratic function. Give the (a) vertex, (b) axis, (c) domain, and (d) range. ƒ(x) = (x - 2)2
Problem 23
Solve each polynomial inequality. Give the solution set in interval notation.
(a) -x(x - 1)(x - 2) ≥ 0
(b) -x(x - 1)(x - 2) > 0
(c) -x(x - 1)(x - 2) ≤ 0
(d) -x(x - 1)(x - 2) < 0
Problem 24
Use synthetic division to perform each division. x7+1 / x+1
Problem 24
Use an end behavior diagram, as shown below, to describe the end behavior of the graph of each polynomial function. ƒ(x)=4x7-x5+x3-1