Back
BackProblem 15
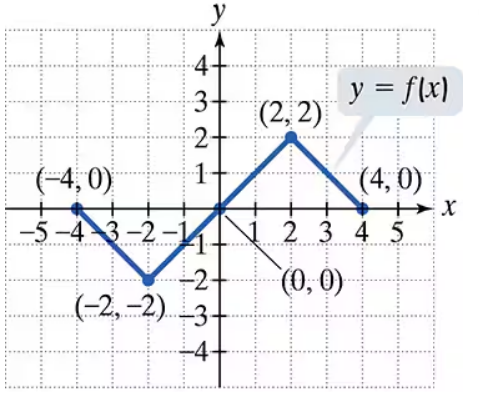
Use the graph of y = f(x) to graph each function g.
g(x) = −ƒ( x/2) +1
Problem 15
Find the distance between each pair of points. If necessary, express answers in simplified radical form and then round to two decimal places. (3√3, √5) and (−√3, 4√5)
Problem 15
The functions in Exercises 11-28 are all one-to-one. For each function, a. Find an equation for f-1(x), the inverse function. b. Verify that your equation is correct by showing that f(ƒ-1 (x)) = = x and ƒ-1 (f(x)) = x. f(x) = 2x + 3
Problem 15
Use the vertical line test to identify graphs in which y is a function of x.

Problem 15
Find the average rate of change of the function from x1 to x2. f(x) = x² + 2x from x1 = 3 to x2 = 5
Problem 15a
Find the domain of each function. f(x) = 1/[4/(x - 1) - 2]
Problem 16
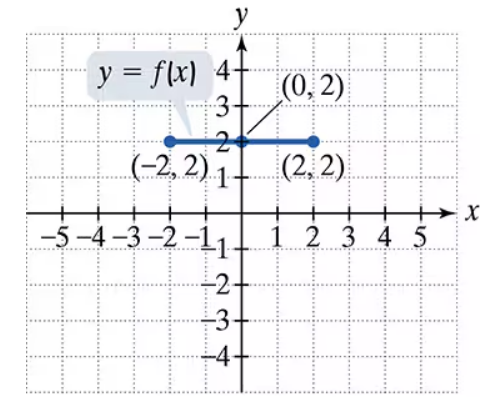
In Exercises 1-16, use the graph of y = f(x) to graph each function g.
g(x) = -f(2x) - 1
Problem 16a
Use the given conditions to write an equation for each line in point-slope form and slope-intercept form. Slope = -5, passing through (-4, -2)
Problem 17
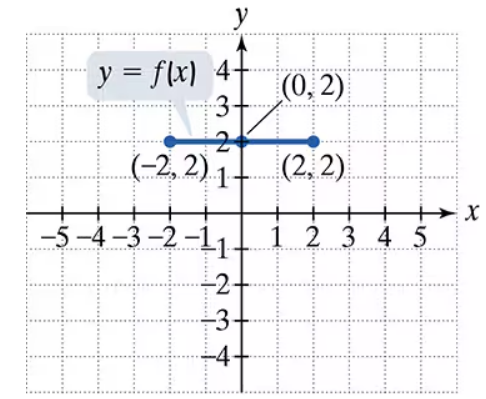
Use the graph of y = f(x) to graph each function g.
g(x) = f(x) - 1
Problem 17
The functions in Exercises 11-28 are all one-to-one. For each function, a. Find an equation for f-1(x), the inverse function. b. Verify that your equation is correct by showing that f(ƒ-1 (x)) = = x and ƒ-1 (f(x)) = x. f(x) = x³ +2
Problem 17
Find the distance between each pair of points. If necessary, express answers in simplified radical form and then round to two decimal places. (7/3, 1/5) and (1/3, 6/5)
Problem 17
Find the average rate of change of the function from x1 to x2. f(x) = √x from x1 = 4 to x2 = 9
Problem 17
In Exercises 11–26, determine whether each equation defines y as a function of x. x = y²
Problem 17a
Find the domain of each function. f(x) = √(x - 3)
Problem 18
Find the distance between each pair of points. If necessary, express answers in simplified radical form and then round to two decimal places. (-1/4, -1/7) and (3/4, 6/7)
Problem 18
Use the graph to determine (a) the function's domain, (b) the function's range, (c) the x-intercepts, if any, (d) the y-intercept, if there is one, (e) intervals on which the function is increasing, decreasing or constant, (f) the missing function values, indicated by question marks, below each graph.

Problem 18a
In Exercises 11–26, determine whether each equation defines y as a function of x. 4x = y²
Problem 19
Find the domain of each function. f(x) = 1/√(x - 3)
Problem 19
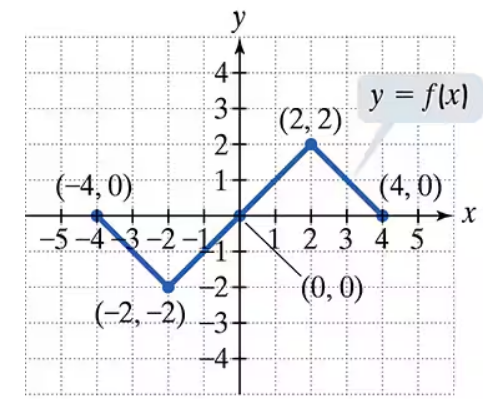
use the graph of y = f(x) to graph each function g.
g(x) = f(x-1)
Problem 19
Find the midpoint of each line segment with the given endpoints. (6, 8) and (2, 4)
Problem 19
Write an equation in slope-intercept form of a linear function f whose graph satisfies the given conditions. The graph of ƒ passes through (−1, 5) and is perpendicular to the line whose equation is x = 6.
Problem 19
The functions in Exercises 11-28 are all one-to-one. For each function, a. Find an equation for f-1(x), the inverse function. b. Verify that your equation is correct by showing that f(ƒ-1 (x)) = = x and ƒ-1 (f(x)) = x. f(x) = (x+2)³
Problem 19a
Determine whether each equation defines y as a function of x. y = √x +4
Problem 20
Write an equation in slope-intercept form of a linear function f whose graph satisfies the given conditions. The graph of ƒ passes through (−2, 6) and is perpendicular to the line whose equation is x = -4.
Problem 20
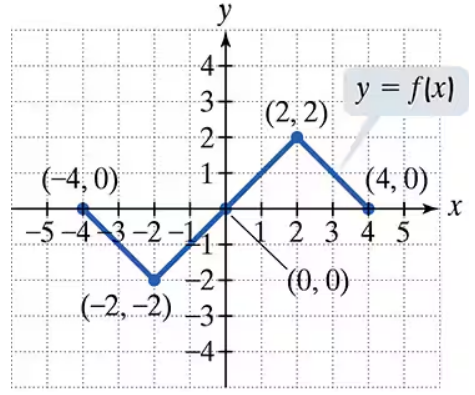
Use the graph of y = f(x) to graph each function g. g(x) = f(x+1)
Problem 20
Determine whether each equation defines y as a function of x.
Problem 20a
Use the given conditions to write an equation for each line in point-slope form and slope-intercept form. Slope = −1, passing through (−4, − 1/4)
Problem 21
Write an equation in slope-intercept form of a linear function f whose graph satisfies the given conditions. The graph of ƒ passes through (−6, 4) and is perpendicular to the line that has an x intercept of 2 and a y-intercept of -4.
Problem 21
Find the midpoint of each line segment with the given endpoints. (-2, -8) and (−6, −2)
Problem 21
Find the domain of each function. f(x) = √(5x+35)