Back
BackProblem 1
Determine which functions are polynomial functions. For those that are, identify the degree.
Problem 1
Solve each polynomial inequality in Exercises 1–42 and graph the solution set on a real number line. Express each solution set in interval notation. (x−4)(x+2)>0
Problem 1
Use the Rational Zero Theorem to list all possible rational zeros for each given function. f(x)=x3+x2−4x−4
Problem 1
In Exercises 1–4, use the vertex and intercepts to sketch the graph of each quadratic function. Give the equation for the parabola's axis of symmetry. Use the graph to determine the function's domain and range.
Problem 1
Find the domain of each rational function. f(x)=5x/(x−4)
Problem 1
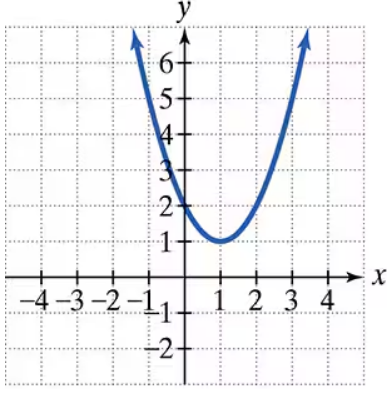
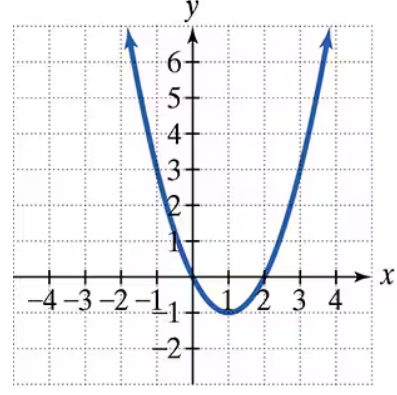
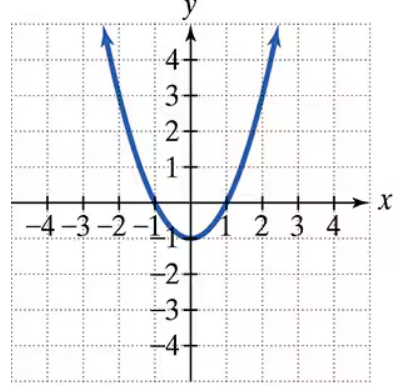
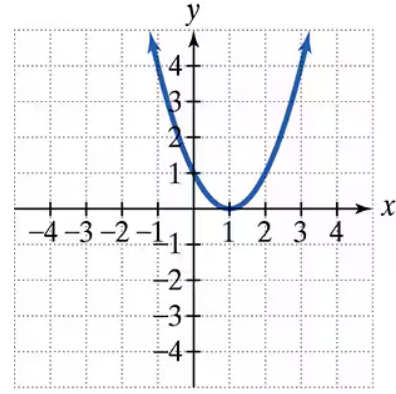
The graph of a quadratic function is given. Write the function's equation, selecting from the following options.
Problem 1
Use the four-step procedure for solving variation problems given on page 447 to solve Exercises 1–10. y varies directly as x. y = 65 when x = 5. Find y when x = 12.
Problem 1a
Divide using long division. State the quotient, and the remainder, r(x). (x2+8x+15)÷(x+5)
Problem 2
Solve each polynomial inequality in Exercises 1–42 and graph the solution set on a real number line. Express each solution set in interval notation. (x+3)(x−5)>0
Problem 2
In Exercises 1–4, use the vertex and intercepts to sketch the graph of each quadratic function. Give the equation for the parabola's axis of symmetry. Use the graph to determine the function's domain and range. f(x) = (x + 4)^2 - 2
Problem 3
Use the four-step procedure for solving variation problems given on page 447 to solve Exercises 1–10. y varies inversely as x. y = 12 when x = 5. Find y when x = 2.
Problem 3
Find the domain of each rational function. g(x)=3x2/(x−5)(x+4)
Problem 3
In Exercises 1–4, use the vertex and intercepts to sketch the graph of each quadratic function. Give the equation for the parabola's axis of symmetry. Use the graph to determine the function's domain and range.
Problem 3
Use the Rational Zero Theorem to list all possible rational zeros for each given function. f(x)=3x4−11x3−x2+19x+6
Problem 3
The graph of a quadratic function is given. Write the function's equation, selecting from the following options.
Problem 3
Determine which functions are polynomial functions. For those that are, identify the degree.
Problem 3a
Divide using long division. State the quotient, and the remainder, r(x). (x3+5x2+7x+2)÷(x+2)
Problem 4
Solve each polynomial inequality in Exercises 1–42 and graph the solution set on a real number line. Express each solution set in interval notation. (x+1)(x−7)≤0
Problem 4
In Exercises 1–10, determine which functions are polynomial functions. For those that are, identify the degree. g(x)=6x7+πx5+2/3 x
Problem 5
Determine which functions are polynomial functions. For those that are, identify the degree.
Problem 5
Use the four-step procedure for solving variation problems given on page 447 to solve Exercises 1–10. y varies directly as x and inversely as the square of z. y = 20 when x = 50 and z = 5. Find y when x = 3 and z = 6.
Problem 5
Divide using long division. State the quotient, and the remainder, .
Problem 5
Find the domain of each rational function. h(x)=(x+7)/(x2−49)
Problem 5
Use the Rational Zero Theorem to list all possible rational zeros for each given function. f(x)=4x4−x3+5x2−2x−6
Problem 5
The graph of a quadratic function is given. Write the function's equation, selecting from the following options.
Problem 5
In Exercises 5–6, use the function's equation, and not its graph, to find (a) the minimum or maximum value and where it occurs. (b) the function's domain and its range.
Problem 6
In Exercises 1–8, use the Rational Zero Theorem to list all possible rational zeros for each given function. f(x)=3x4−11x3−3x2−6x+8
Problem 7
Solve each polynomial inequality in Exercises 1–42 and graph the solution set on a real number line. Express each solution set in interval notation. x2+5x+4>0
Problem 7
The graph of a quadratic function is given. Write the function's equation, selecting from the following options.
Problem 7
Divide using long division. State the quotient, and the remainder, .