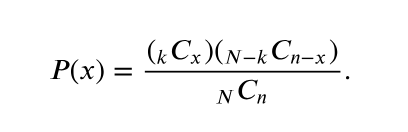Back
BackProblem 4.1.21b
Finding Probabilities Use the probability distribution you made in Exercise 19 to find the probability of randomly selecting a household that has (b) two or more HD televisions
Problem 4.3.28b
Hypergeometric Distribution Binomial experiments require that any sampling be done with replacement because each trial must be independent of the others. The hypergeometric distribution also has two outcomes: success and failure. The sampling, however, is done without replacement. For a population of N items having k successes and failures, the probability of selecting a sample of size that has successes and failures is given by
In a shipment of 15 microchips, 2 are defective and 13 are not defective. A sample of three microchips is chosen at random. Use the above formula to find the probability that (b) one microchip is defective and two are not defective
Problem 4.2.37b
Unusual Events In Exercises 37 and 38, find the indicated probabilities. Then determine if the event is unusual. Explain your reasoning.
Rock-Paper-Scissors The probability of winning a game of rock-paper-scissors is 1/3. You play nine games of rock-paper-scissors. Find the probability that the number of games you win is (b) more than five
Problem 4.3.26b
Using a Distribution to Find Probabilities In Exercises 11–26, find the indicated probabilities using the geometric distribution, the Poisson distribution, or the binomial distribution. Then determine whether the events are unusual. If convenient, use a table or technology to find the probabilities.
Oil Tankers In the month of June 2021, 240 oil tankers stop at a port city. No oil tanker visits more than once. Find the probability that the number of oil tankers that stop on any given day in June is (b) at most three
Problem 4.2.41b
Manufacturing An assembly line produces 10,000 automobile parts. Twenty percent of the parts are defective. An inspector randomly selects 10 of the parts
b. Because the sample is only 0.1% of the population, treat the events as independent and use the binomial probability formula to approximate the probability that none of the selected parts are defective.
Problem 4.3.18b
Using a Distribution to Find Probabilities In Exercises 11–26, find the indicated probabilities using the geometric distribution, the Poisson distribution, or the binomial distribution. Then determine whether the events are unusual. If convenient, use a table or technology to find the probabilities.
Living Donor Transplants The mean number of organ transplants from living donors performed per day in the United States in 2020 was about 16. Find the probability that the number of organ transplants from living donors performed on any given day is (b) at least eight (Source: Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network)
Problem 4.3.18c
Using a Distribution to Find Probabilities In Exercises 11–26, find the indicated probabilities using the geometric distribution, the Poisson distribution, or the binomial distribution. Then determine whether the events are unusual. If convenient, use a table or technology to find the probabilities.
Living Donor Transplants The mean number of organ transplants from living donors performed per day in the United States in 2020 was about 16. Find the probability that the number of organ transplants from living donors performed on any given day is (c) no more than 10. (Source: Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network)
Problem 4.1.21c
Finding Probabilities Use the probability distribution you made in Exercise 19 to find the probability of randomly selecting a household that has (c) from one to three HD televisions,
Problem 4.2.37c
Unusual Events In Exercises 37 and 38, find the indicated probabilities. Then determine if the event is unusual. Explain your reasoning.
Rock-Paper-Scissors The probability of winning a game of rock-paper-scissors is 1/3. You play nine games of rock-paper-scissors. Find the probability that the number of games you win is (c) less than two.
Problem 4.3.28c
Hypergeometric Distribution Binomial experiments require that any sampling be done with replacement because each trial must be independent of the others. The hypergeometric distribution also has two outcomes: success and failure. The sampling, however, is done without replacement. For a population of N items having k successes and failures, the probability of selecting a sample of size that has successes and failures is given by
In a shipment of 15 microchips, 2 are defective and 13 are not defective. A sample of three microchips is chosen at random. Use the above formula to find the probability that (c) two microchips are defective and one is not defective.
Problem 4.3.26c
Using a Distribution to Find Probabilities In Exercises 11–26, find the indicated probabilities using the geometric distribution, the Poisson distribution, or the binomial distribution. Then determine whether the events are unusual. If convenient, use a table or technology to find the probabilities.
Oil Tankers In the month of June 2021, 240 oil tankers stop at a port city. No oil tanker visits more than once. Find the probability that the number of oil tankers that stop on any given day in June is (c) more than eight.
Problem 4.1.21d
Finding Probabilities Use the probability distribution you made in Exercise 19 to find the probability of randomly selecting a household that has (d) at most two HD televisions.