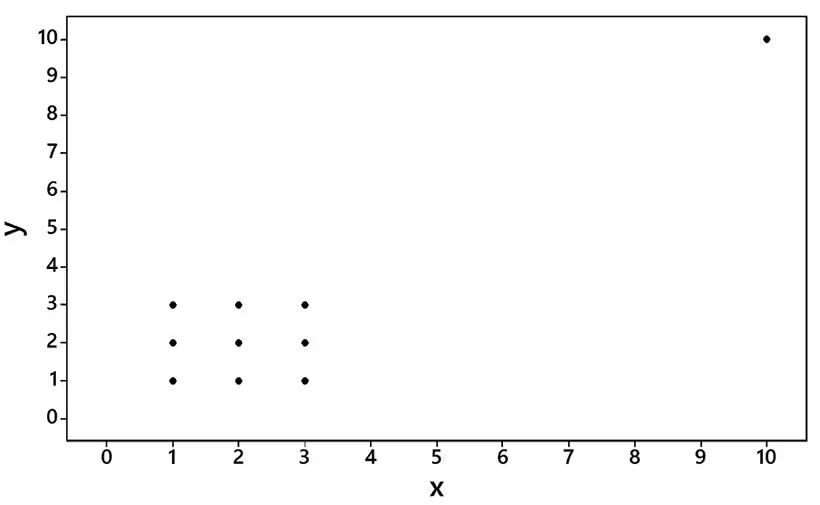
Boxplots from Large Data Sets in Appendix B. In Exercises 33–36, use the given data sets in Appendix B. Use the boxplots to compare the two data sets.
Pulse Rates Use the same scale to construct boxplots for the pulse rates of males and females from Data Set 1 “Body Data” in Appendix B.