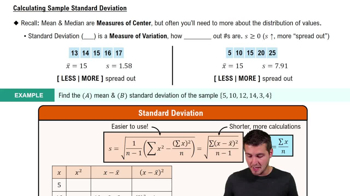
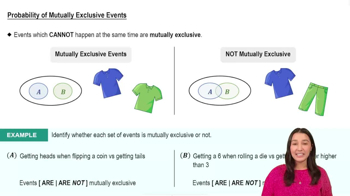
Finding Bone Density Scores. In Exercises 37–40 assume that a randomly selected subject is given a bone density test. Bone density test scores are normally distributed with a mean of 0 and a standard deviation of 1. In each case, draw a graph, then find the bone density test score corresponding to the given information. Round results to two decimal places.
Find P99, the 99th percentile. This is the bone density score separating the bottom 99% from the top 1%.