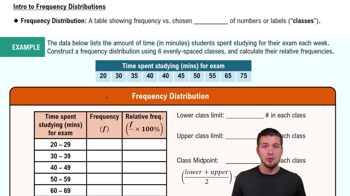
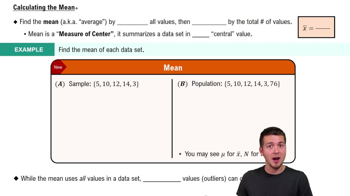
In Exercises 5–8, assume that the Poisson distribution applies; assume that the mean number of Atlantic hurricanes in the United States is 5.5 per year, as in Example 1; and proceed to find the indicated probability.
a. Find the probability that in a year, there will be 10 hurricanes.