F Test Statistic
a. If s2,1 represents the larger of two sample variances, can the F test statistic ever be less than 1?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: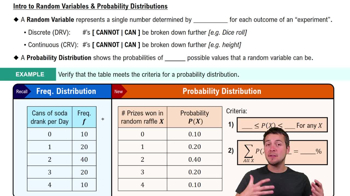

 6:21m
6:21mMaster Step 1: Write Hypotheses with a bite sized video explanation from Patrick
Start learning