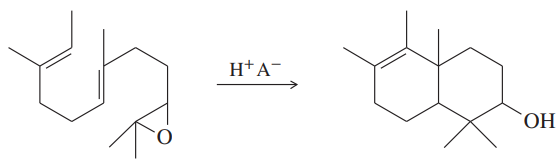Back
BackProblem 45c
Show how you would synthesize the following ethers in good yield from the indicated starting materials and any additional reagents needed.
(c) 2-ethoxyoctane from an octene
Problem 45d
Show how you would synthesize the following ethers in good yield from the indicated starting materials and any additional reagents needed.
(d) 1-methoxydecane from a decene
Problem 45e
Show how you would synthesize the following ethers in good yield from the indicated starting materials and any additional reagents needed.
(e) 1-ethoxy-1-methylcyclohexane from 2-methylcyclohexanol
Problem 45f
Show how you would synthesize the following ethers in good yield from the indicated starting materials and any additional reagents needed.
(f) trans-2,3-epoxyoctane from octan-2-ol
Problem 46
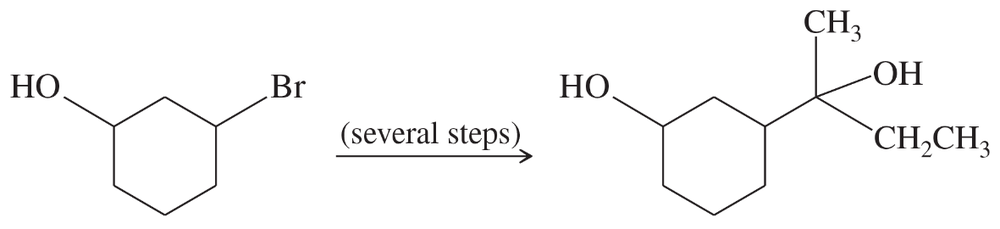
Show how you would convert 3-bromocyclohexanol to the following diol. You may use any additional reagents you need.
Problem 47
There are two different ways of making 2-ethoxyoctane from octan-2-ol using the Williamson ether synthesis. When pure (–)-octan-2-ol of specific rotation -8.24° is treated with sodium metal and then ethyl iodide, the product is 2-ethoxyoctane with a specific rotation of -15.6°. When pure (–)-octan-2-ol is treated with tosyl chloride and pyridine and then with sodium ethoxide, the product is also 2-ethoxyoctane. Predict the rotation of the 2-ethoxyoctane made using the tosylation/sodium ethoxide procedure, and propose a detailed mechanism to support your prediction.
Problem 49
An acid-catalyzed reaction was carried out using methyl cellosolve (2-methoxyethanol) as the solvent. When the 2-methoxyethanol was redistilled, a higher-boiling fraction (bp 162°C) was also recovered. The mass spectrum of this fraction showed the molecular weight to be 134. The IR and NMR spectra are shown here. Determine the structure of this compound, and propose a mechanism for its formation.
<IMAGE>
Problem 50a,b
Propylene oxide is a chiral molecule. Hydrolysis of propylene oxide gives propylene glycol, another chiral molecule.
(a) Draw the enantiomers of propylene oxide.
(b) Propose a mechanism for the acid-catalyzed hydrolysis of pure (R)-propylene oxide.
Problem 51
A compound of molecular formula C8H8O gives the IR and NMR spectra shown here. Propose a structure, and show how it is consistent with the observed absorptions.
<IMAGE>
Problem 53
Under the right conditions, the following acid-catalyzed double cyclization proceeds in remarkably good yields. Propose a mechanism. Does this reaction resemble a biological process you have seen?
Problem 54d,e
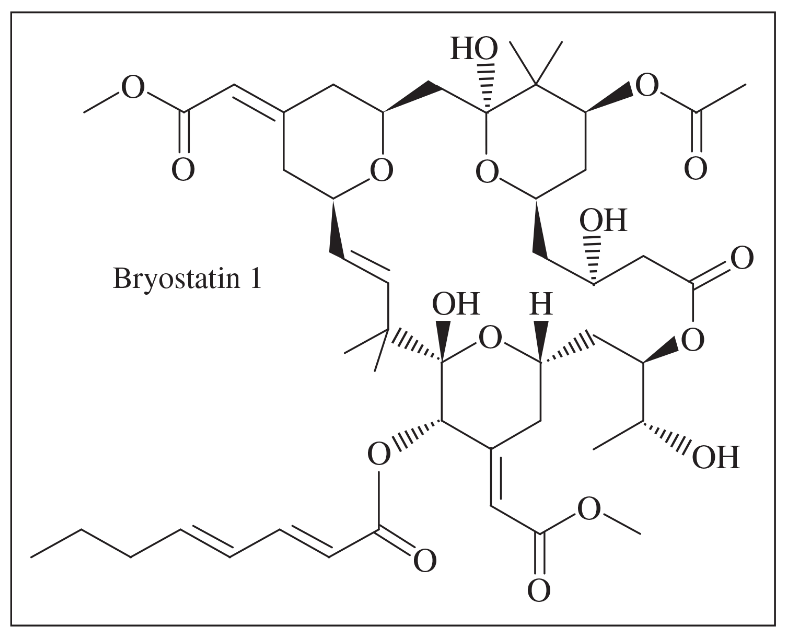
One of the crowning achievements of natural products synthesis was Bryostatin 1, published by Professor Gary Keck (University of Utah; Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2011, 133, 744–747). The Bryostatins are a family of compounds isolated from aquatic invertebrates known as Bryozoans. The compounds are of interest for a variety of biological effects, including anti-cancer activity and reversing brain damage in rodents.
(d) How many chiral centers are in this molecule?
(e) Using the number of chiral centers you reported in part (d), calculate the number of stereoisomers possible at these chiral centers. (Ignore stereoisomers at double bonds.)
Problem 55
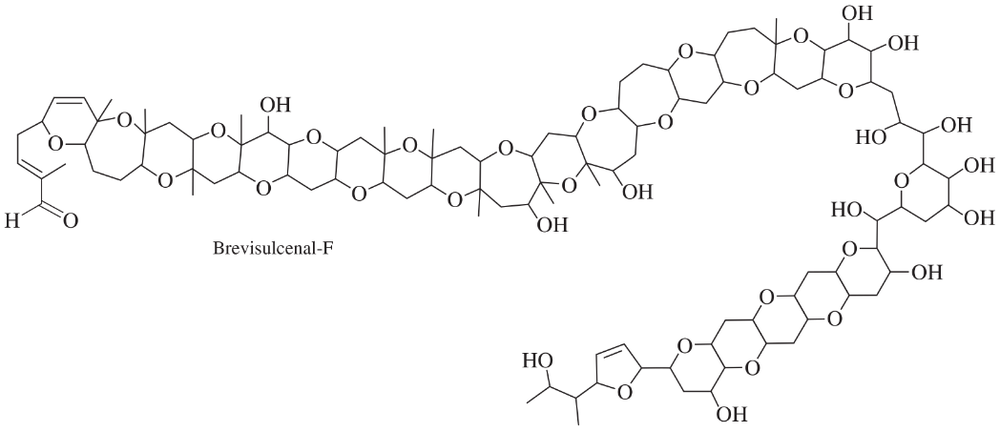
In 2012, a group led by Professor Masayuki Satake of the University of Tokyo reported the isolation and structure determination of a toxin from a marine algal bloom that decimated the fish population off the New Zealand coast in 1998. Extensive mass spectrometry and NMR experiments ultimately led to the structure shown below, named Brevisulcenal-F. (See Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2012, 134, 4963–4968.) This structure holds the record for the largest number of fused rings, at 17.
(a) How many ether groups are present?
(b) How many alcohol groups are present? Classify the alcohols as 1° or 2° or 3°.
(c) Are there any other oxygen-containing functional groups? Which, if any?