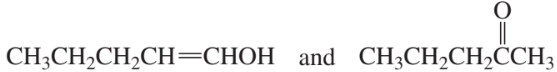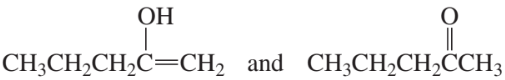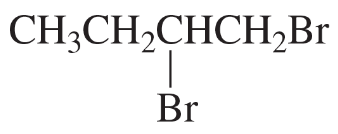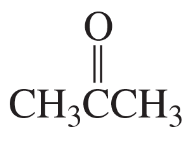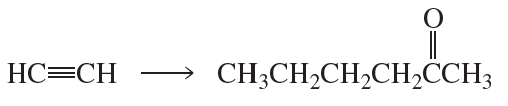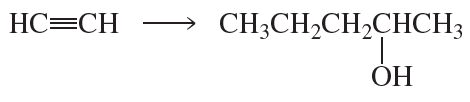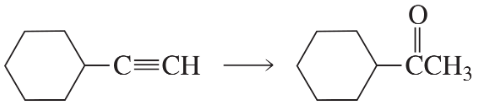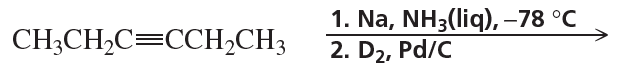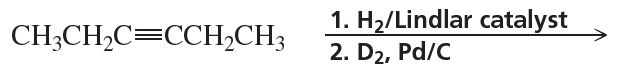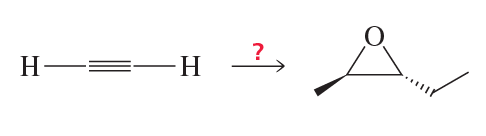Back
Back Bruice 8th Edition
Bruice 8th Edition Ch.7 - The Reactions of Alkynes An Introduction to Multistep Synthesis
Ch.7 - The Reactions of Alkynes An Introduction to Multistep SynthesisProblem 43(1)
a. Starting with 3-methyl-1-butyne, how can you prepare the following alcohols?
1. 2-methyl-2-butanol
b. In each case, a second alcohol would also be obtained. What alcohol would it be?
Problem 44a,b
Which of the following names are correct? Correct those that are not correct.
a. 4-heptyne
b. 2-ethyl-3-hexyne
Problem 44c,d
Which of the following names are correct? Correct those that are not correct.
c. 4-chloro-2-pentyne
d. 2,3-dimethyl-5-octyne
Problem 44e,f
Which of the following names are correct? Correct those that are not correct.
e. 4,4-dimethyl-2-pentyne
f. 2,5-dimethyl-3-hexyne
Problem 45d,e
Which of the following pairs are keto–enol tautomers?
d.
e.
Problem 46a
How can the following compounds be prepared using ethyne as the starting material?
a.
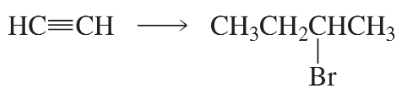
Problem 46b
How can the following compounds be prepared using ethyne as the starting material?
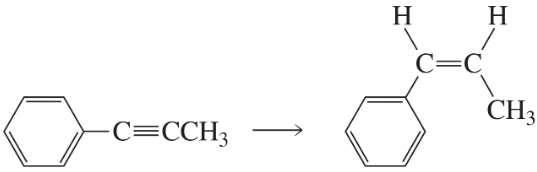
b.
Problem 46c
How can the following compounds be prepared using ethyne as the starting material?
c.
Problem 46e
How can the following compounds be prepared using ethyne as the starting material?
e.
Problem 46f
How can the following compounds be prepared using ethyne as the starting material?
f.
Problem 47
Do the equilibria of the following acid–base reactions lie to the right or the left? (The pKa of H2O2 is 11.6.)
HOOH + HO− ⇌ HOO− + H2O
RC☰CH + HOO− ⇌ RC☰C− + HOOH
Problem 48c,d
What is each compound's systematic name?
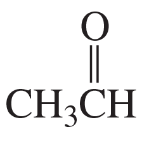
c.
d.
Problem 49a
What stereoisomers are obtained when 2-butyne undergoes each of the following reaction sequences?
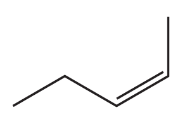
a. 1. H2/Lindlar catalyst 2. Br2/CH2Cl2
Problem 49c
What stereoisomers are obtained when 2-butyne undergoes each of the following reaction sequences?
c. 1. Cl2/CH2Cl2 2. Br2/CH2Cl2
Problem 50a
Show how the following compounds can be synthesized starting with ethyne:
a. cis-2-octene
Problem 50b
Show how the following compounds can be synthesized starting with ethyne:
b. trans-3-heptene
Problem 52a
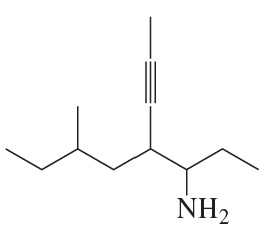
Show how each of the following compounds can be prepared using the given starting material, any needed inorganic reagents, and any organic compound that has no more than four carbons:
a.
Problem 52b
Show how each of the following compounds can be prepared using the given starting material, any needed inorganic reagents, and any organic compound that has no more than four carbons:
b.
Problem 52c
Show how each of the following compounds can be prepared using the given starting material, any needed inorganic reagents, and any organic compound that has no more than four carbons:
c.
Problem 52e
Show how each of the following compounds can be prepared using the given starting material, any needed inorganic reagents, and any organic compound that has no more than four carbons:
e.
Problem 52f
Show how each of the following compounds can be prepared using the given starting material, any needed inorganic reagents, and any organic compound that has no more than four carbons:
f.
Problem 53
A chemist is planning to synthesize 3-octyne by adding 1-bromobutane to the product obtained from the reaction of 1-butyne with sodium amide. Unfortunately, however, he forgot to order 1-butyne. How else can he prepare 3-octyne?
Problem 54
a. Explain why a single pure product is obtained from hydroboration–oxidation of 2-butyne, whereas two products are obtained from hydroboration–oxidation of 2-pentyne.
b. Name two other internal alkynes that yield only one product upon hydroboration–oxidation.
Problem 55a
What stereoisomers are obtained from the following reactions?
Problem 55b
What stereoisomers are obtained from the following reactions?
b.
Problem 56
Explain why, in hydroboration–oxidation, HO− and HOOH cannot be added until after the hydroboration reaction is over.
Problem 57a
Starting with ethyne, describe how the following compounds can be synthesized:
a. (3S,4R)-4-bromo-3-hexanol and (3R,4S)-4-bromo-3-hexanol
Problem 58
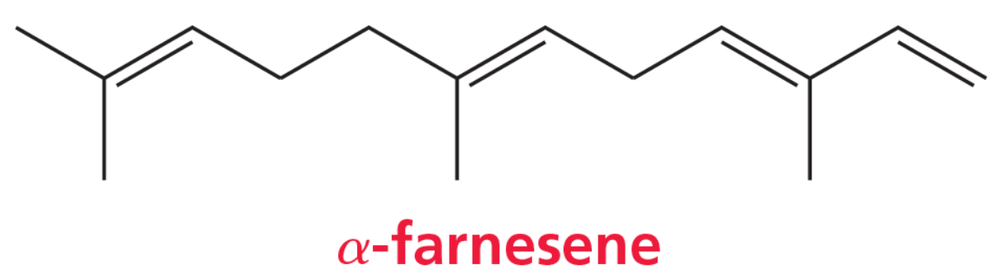
α-Farnesene is a dodecatetraene found in the waxy coating of apple skins. What is its systematic name? Include E and Z where necessary to indicate the configuration of the double bonds.
Problem 59
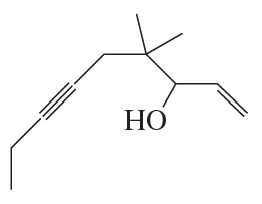
Show how the following compound can be prepared from the given starting material. Draw the structure of the compound that is formed in each step of the synthesis.