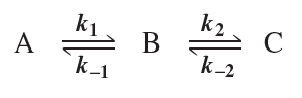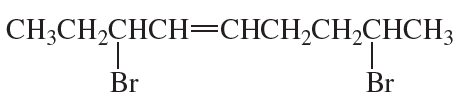Back
Back Bruice 8th Edition
Bruice 8th Edition Ch.5 - Alkenes:Structure, Nomenclature, and an Introduction to Reactivity Thermodynamics and Kinetics
Ch.5 - Alkenes:Structure, Nomenclature, and an Introduction to Reactivity Thermodynamics and KineticsProblem 18b
Calculate ∆G° for the conversion of “axial” methylcyclohexane to “equatorial” methylcyclohexane at 25 °C.
Problem 19
The ∆G° for conversion of “axial” fluorocyclohexane to “equatorial” fluorocyclohexane at 25 °C is -0.25kcal/mol. Calculate the percentage of fluorocyclohexane molecules that have the fluoro substituent in an equatorial position at equilibrium.
Problem 20a
Calculate the percentage of isopropylcyclohexane molecules that have the isopropyl substituent in an equatorial position at equilibrium. (Its ∆G° value at 25 °C is -2.1 kcal/mol.)
Problem 20b
Why is the percentage of molecules with the substituent in an equatorial position greater for isopropylcyclohexane than for fluorocyclohexane?
Problem 21
a. For which reaction in each set will ∆S° be more significant?
b. For which reaction will ∆S° be positive?
1. A ⇌ B or A + B ⇌ C
2. A ⇌ B + C or A + B ⇌ C + D
Problem 22
a. For a reaction with ∆H° = -12 kcal/mol and ∆S° = 0.01 kcal mol-1 K-1, calculate the ∆G° and the equilibrium constant at:
1. 30 °C and 2. 150 °C.
b. How does ∆G° change as T increases?
c. How does Keq change as T increases?
Problem 24a
What alkene would you start with if you wanted to synthesize
a. pentane?
Problem 24b
What alkene would you start with if you wanted to synthesize
b. ethylcyclopentane?
Problem 25a,b
How many different alkenes can be hydrogenated to form
a. butane?
b. 3-methylpentane?
Problem 26
The same alkane is obtained from the catalytic hydrogenation of both alkene A and alkene B. The heat of hydrogenation of alkene A is 29.8 kcal/mol, and the heat of hydrogenation of alkene B is 31.4 kcal/mol. Which alkene is more stable?
Problem 28
Rank the following compounds from most stable to least stable:
trans-3-hexene, cis-3-hexene, cis-2,5-dimethyl-3-hexene, (Z)-3,4-dimethyl-3-hexene
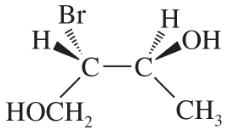
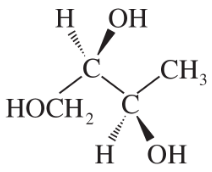
Problem 28c,d
Convert the following perspective formulas to Fischer projections.
(c)
(d)
Problem 30
Draw a reaction coordinate diagram for a reaction in which
a. the product is thermodynamically unstable and kinetically unstable.
b. the product is thermodynamically unstable and kinetically stable.
Problem 31b
The rate of the reaction of methyl chloride with hydroxide ion is linearly dependent on both the concentration of methyl chloride and the concentration hydroxide ion. At 30 °C, the constant (k) for the reaction is 1.0 × 10-5 M-1 s-1
b. If the concentration of methyl chloride is decreased to 0.010 M, what will be the effect on
1. the rate of the reaction?
2. the rate constant for the reaction?
Problem 32
The rate constant for a reaction can be increased by ______ the stability of the reactant or by ______ the stability of the transition state.
Problem 33a
From the Arrhenius equation, predict how
a. increasing the experimental activation energy affects the rate constant for a reaction.
Problem 33b
From the Arrhenius equation, predict how
b. increasing the temperature affects the rate constant for a reaction.
Problem 34a,b
a. Which reaction has a greater equilibrium constant: one with a rate constant of 1 × 10-3 sec-1 for the forward reaction and a rate constant of 1 × 10-5 sec-1 for the reverse reaction, or one with a rate constant of 1 × 10-2 sec-1 for the forward reaction and a rate constant of 1 × 10-3 sec-1 for the reverse reaction?
b. If both reactions start with a reactant concentration of 1.0 M, which reaction will form the most product when the reactions have reached equilibrium?
Problem 35
Draw a reaction coordinate diagram for a two-step reaction in which the first step is endergonic, the second step is exergonic, and the overall reaction is endergonic. Label the reactants, products, intermediates, and transition states.
Problem 36
a. Which step in the reaction coordinate diagram shown here has the greatest free energy of activation in the forward direction?
b. Is the first-formed intermediate more apt to revert to reactants or go on to form products?
c. Which step is the rate-determining step of the reaction?
<IMAGE>
Problem 37a-d
Draw a reaction coordinate diagram for the following reaction in which C is the most stable and B the least stable of the three species and the transition state going from A to B is more stable than the transition state going from B to C:
a. How many intermediates are there?
b. How many transition states are there?
c. Which step has the greater rate constant in the forward direction?
d. Which step has the greater rate constant in the reverse direction?
Problem 38
Which of the following parameters would be different for a reaction carried out in the presence of a catalyst compared with the same reaction carried out in the absence of a catalyst?
∆G°, ∆H‡, Ea, ∆S‡, ∆H°, Keq, ∆G‡, ∆S°, k
Problem 39a
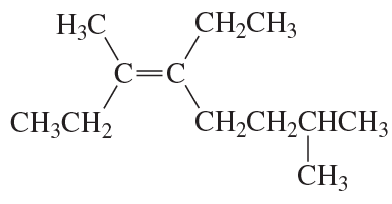
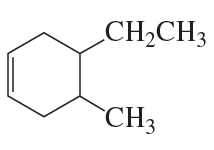
What is each compound's systematic name?
a.
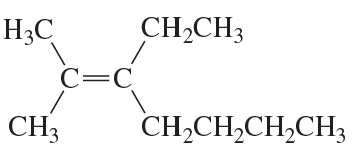
Problem 39b
What is each compound's systematic name?
b.
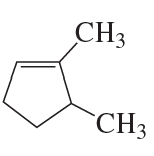
Problem 39c
What is each compound's systematic name?
c.
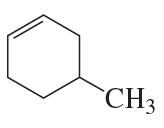
Problem 39d,e,f
What is each compound's systematic name?
d.
e.
f.
Problem 41
Draw the structure of a hydrocarbon that has six carbon atoms and
a. three vinylic hydrogens and two allylic hydrogens.
b. three vinylic hydrogens and one allylic hydrogen.
c. three vinylic hydrogens and no allylic hydrogens.
Problem 42a,b,c
Draw the condensed structure for each of the following:
a. (Z)-1,3,5-tribromo-2-pentene
b. (Z)-3-methyl-2-heptene
c. (E)-1,2-dibromo-3-isopropyl-2-hexene
Problem 42d,e,f
Draw the condensed structure for each of the following:
d. vinyl bromide
e. 1,2-dimethylcyclopentene
f. diallylamine
Problem 43d,e,f
Draw the skeletal structures for the compounds in Problem 42.
d. vinyl bromide
e. 1,2-dimethylcyclopentene
f. diallylamine