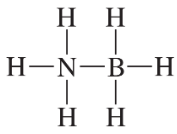Back
Back Bruice 8th Edition
Bruice 8th Edition Ch.1 - Remembering General Chemistry:Electronic Structure and Bonding (Part 1)
Ch.1 - Remembering General Chemistry:Electronic Structure and Bonding (Part 1)Problem 1a
Oxygen has three isotopes, 16O, 17O, and 18O. The atomic number of oxygen is 8. How many protons and neutrons does each of the isotopes have?
Problem 2
a. How many protons do the following species have?
b. How many electrons does each have?
- Na+
- Ar
- Cl-
Problem 3
Chlorine has two isotopes, 35Cl and 37Cl; 75.77% of chlorine is 35Cl, and 24.23% is 37Cl. The atomic mass of 35Cl is 34.969 amu, and the atomic mass of 37Cl is 36.966 amu. What is the atomic mass of chlorine?
Problem 4a,b
How many valence electrons do the following atoms have?
a. boron
b. nitrogen
Problem 5a
Write the ground-state electronic configuration for chlorine (atomic number 17), bromine (atomic number 35), and iodine (atomic number 53).
Problem 5b
How many valence electrons do chlorine, bromine, and iodine have?
Problem 6a,b
Look at the relative positions of each pair of atoms listed here in the periodic table. How many core electrons does each have? How many valence electrons does each have?
a. carbon and silicon
b. oxygen and sulfur
Problem 6c,d
Look at the relative positions of each pair of atoms listed here in the periodic table. How many core electrons does each have? How many valence electrons does each have?
c. nitrogen and phosphorus
d. magnesium and calcium
Problem 7
a. Find potassium (K) in the periodic table and predict how many valence electrons it has.
b. What orbital does the unpaired electron occupy?
Problem 15a,b
An atom with a formal charge does not necessarily have more or less electron density than the atoms in the molecule without formal charges. We can see this by examining the potential maps for H2O, H3O+, and HO−.
<IMAGE>
a. Which atom bears the formal negative charge in the hydroxide ion?
b. Which atom has the greater electron density in the hydroxide ion?
Problem 15c,d
An atom with a formal charge does not necessarily have more or less electron density than the atoms in the molecule without formal charges. We can see this by examining the potential maps for H2O, H3O+, and HO−.
<IMAGE>
c. Which atom bears the formal positive charge in the hydronium ion?
d. Which atom has the least electron density in the hydronium ion?
Problem 16a,b
Give each atom the appropriate formal charge:
a.
b.
Problem 16c,d
Give each atom the appropriate formal charge:
c.
d.
Problem 17d
Draw the Lewis structure for each of the following:
d. +C2H5
Problem 17e
Draw the Lewis structure for each of the following:
e. CH3N+H3
Problem 21
Which of the atoms in the molecular models in [Problem 20] have
<IMAGE>
a. three lone pairs?
b. two lone pairs?
c. one lone pair?
d. no lone pairs?
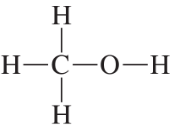
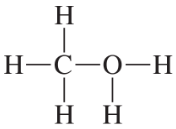
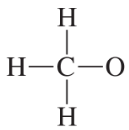
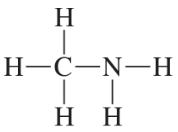
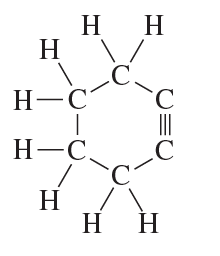
Problem 23
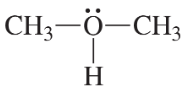
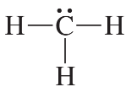
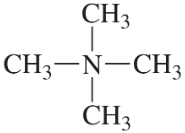
Convert the models in Problem 20 to skeletal structures.
a. <IMAGE>
b. <IMAGE>
c. <IMAGE>
d. <IMAGE>
Problem 24
Draw the following orbitals:
a. 3s orbital
b. 4s orbital
c. 3p orbital
Problem 25
Predict whether He2+ exists.
Problem 26a,b
Indicate the kind of molecular orbital (σ, σ*, π, or π*) that results when the two atomic orbitals are combined:
a. <IMAGE>
b. <IMAGE>
Problem 38(1)
a. Which bond would be longer?
b. Which bond would be stronger?
1. C—Cl or C—I
Problem 38(2)
a. Which bond would be longer?
b. Which bond would be stronger?
2. C—C or C—Cl
Problem 38(3)
a. Which bond would be longer?
b. Which bond would be stronger?
3. H—Cl or H—F
Problem 41
Which of the bonds in a carbon–oxygen double bond has more effective orbital–orbital overlap: the σ bond or the π bond?
Problem 49b
Draw a Lewis structure for each of the following:
b. CO32−
Problem 54a
Draw the ground-state electronic configuration for each of the following:
a. Mg
Problem 54b
Draw the ground-state electronic configuration for each of the following:
b. Ca2+
Problem 63a,b
Draw the missing lone-pair electrons and assign the missing formal charges for the following:
a.
b.
Problem 63c,d
Draw the missing lone-pair electrons and assign the missing formal charges for the following:
c.
d.
Problem 75
Explain why the following compound is not stable: