Textbook Question
Why do chemical reactions in the body require enzymes?

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
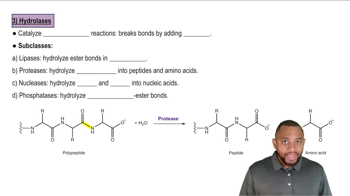
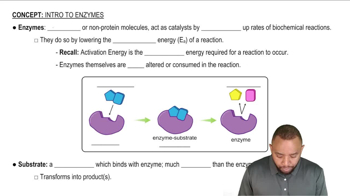

Why do chemical reactions in the body require enzymes?
What is the reactant for each of the following enzymes?
a. galactase
What is the name of the class of enzymes that would catalyze each of the following reactions?
c. converting glucose (C6H12O6) to fructose (C6H12O6).
What is the name of the class of enzymes that would catalyze each of the following reactions?
c. splitting peptide bonds in proteins
Match the terms (1) enzyme–substrate complex, (2) enzyme, and (3) substrate with each of the following:
b. the combination of an enzyme with the substrate
Match the terms (1) enzyme–substrate complex, (2) enzyme, and (3) substrate with each of the following:
a. has a tertiary structure that recognizes the substrate