What is the reactant for each of the following enzymes?
a. galactase

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

What is the reactant for each of the following enzymes?
a. galactase
What is the name of the class of enzymes that would catalyze each of the following reactions?
c. converting glucose (C6H12O6) to fructose (C6H12O6).
What is the name of the class of enzymes that would catalyze each of the following reactions?
a. addition of water to a double bond
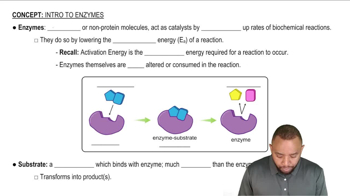
Match the terms (1) enzyme–substrate complex, (2) enzyme, and (3) substrate with each of the following:
b. the combination of an enzyme with the substrate
Match the terms (1) enzyme–substrate complex, (2) enzyme, and (3) substrate with each of the following:
a. has a tertiary structure that recognizes the substrate
Match the terms (1) active site, (2) lock-and-key model, and (3) induced-fit model with each of the following:
a. the portion of an enzyme where catalytic activity occurs