Textbook Question
If a blood test indicates a high level of ALT, what could be the cause?
1
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
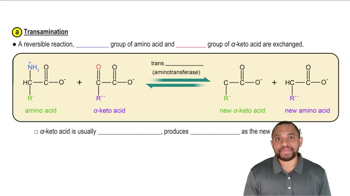
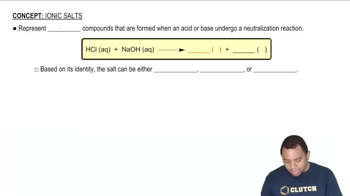
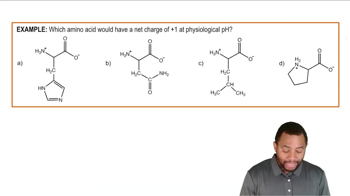
If a blood test indicates a high level of ALT, what could be the cause?
Consider the amino acids lysine, valine, and aspartate in an enzyme. State which of these amino acids have R groups that would:
b. be found in hydrophilic regions
Consider the amino acids lysine, valine, and aspartate in an enzyme. State which of these amino acids have R groups that would:
c. form hydrogen bonds
Consider the amino acids histidine, phenylalanine, and serine in an enzyme. State which of these amino acids have R groups that would:
d. form salt bridges