Textbook Question
Identify each of the following compounds as an aldehyde or a ketone:
a.

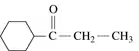
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Identify each of the following compounds as an aldehyde or a ketone:
a.
Identify each of the following compounds as an aldehyde or a ketone:
c.
Identify each of the following compounds as an aldehyde or a ketone:
d.
Write the common name for each of the following:
a. <IMAGE>
Write the common name for each of the following:
b. <IMAGE>
Write the common name for each of the following:
c. <IMAGE>