Textbook Question
Isomaltose, obtained from the breakdown of starch, has the following Haworth structure:
d. Is this the α or β isomer of isomaltose?

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Isomaltose, obtained from the breakdown of starch, has the following Haworth structure:
d. Is this the α or β isomer of isomaltose?
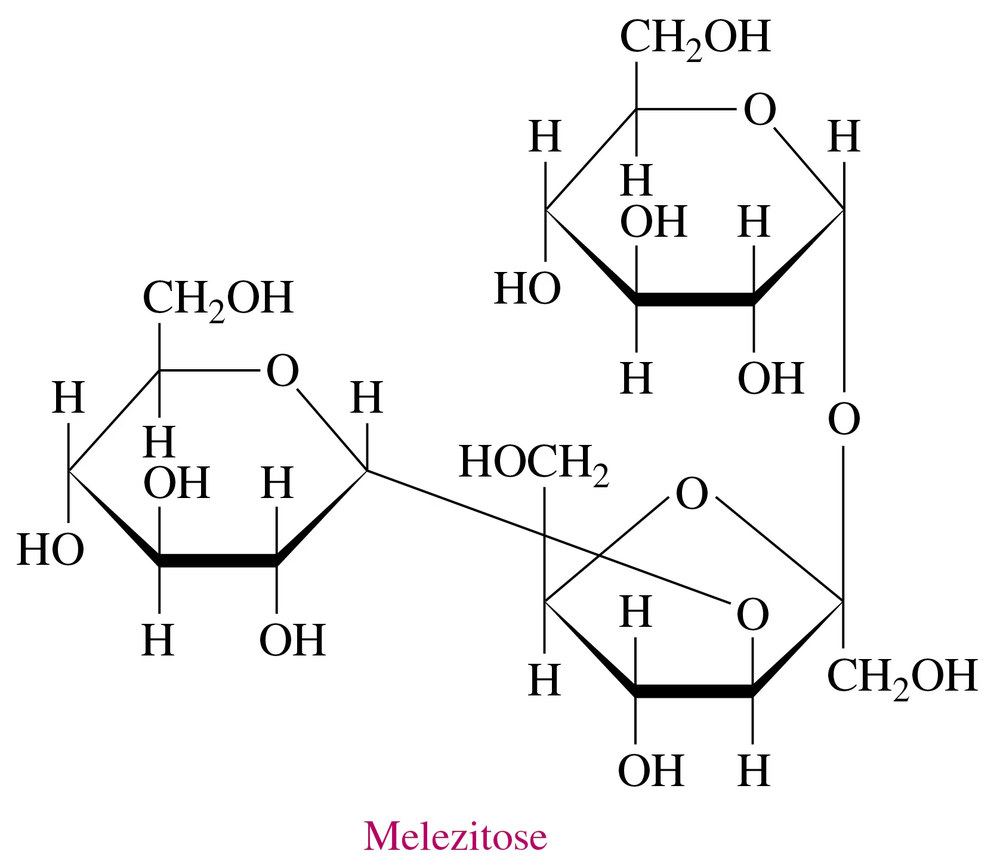
Melezitose, a carbohydrate secreted by insects, has the following Haworth structure:
a. Is melezitose a mono-, di-, or trisaccharide?
Melezitose, a carbohydrate secreted by insects, has the following Haworth structure:
b. What monosaccharides are present in melezitose?
What are the disaccharides and polysaccharides present in each of the following?
a. <IMAGE>
What are the disaccharides and polysaccharides present in each of the following?
a. <IMAGE>
Identify each of the following pairs of Fischer projections as enantiomers or identical compounds:
a.