Back
BackProblem 1c
Use the kinetic molecular theory of gases to explain each of the following:
c. Gases have low densities.
Problem 2b
Use the kinetic molecular theory of gases to explain each of the following:
b. The air in a hot-air balloon is heated to make the balloon rise.
Problem 2c
Use the kinetic molecular theory of gases to explain each of the following:
c. You can smell the odor of cooking onions from far away.
Problem 7b
A tank contains oxygen (O2) at a pressure of 2.00 atm. What is the pressure in the tank in terms of the following units?
b. lb/in.2
Problem 7d
A tank contains oxygen (O2) at a pressure of 2.00 atm. What is the pressure in the tank in terms of the following units?
d. kPa
Problem 8b
On a climb up Mount Whitney, the atmospheric pressure drops to 467 mmHg. What is the pressure in terms of the following units?
b. torr
Problem 8d
On a climb up Mount Whitney, the atmospheric pressure drops to 467 mmHg. What is the pressure in terms of the following units?
d. Pa
Problem 23a
Use the words inspiration and expiration to describe the part of the breathing cycle that occurs as a result of each of the following:
a. The diaphragm contracts.
Problem 24c
Use the words inspiration and expiration to describe the part of the breathing cycle that occurs as a result of each of the following:
c. The pressure within the lungs is higher than that of the atmosphere.
Problem 31
A gas sample has a volume of 0.256 L with an unknown temperature. The same gas has a volume of 0.198 L when the temperature is 32 °C, with no change in the pressure or amount of gas. What was the initial temperature, in degrees Celsius, of the gas?
Problem 42
Rearrange the variables in the combined gas law to solve for P2.
Problem 44a
A sample of argon gas has a volume of 735 mL at a pressure of 1.20 atm and a temperature of 112 °C. What is the final volume of the gas, in milliliters, when the pressure and temperature of the gas sample are changed to the following, if the amount of gas does not change?
a. 658 mmHg and 281 K
Problem 52a
Use the molar volume to calculate each of the following at STP:
a. the number of moles of CO2 in 4.00 L of CO2 gas
Problem 54
Suppose a mixture contains helium and oxygen gases. If the partial pressure of helium is the same as the partial pressure of oxygen, what do you know about the number of helium atoms compared to the number of oxygen molecules? Explain.
Problem 59a
In certain lung ailments such as emphysema, there is a decrease in the ability of oxygen to diffuse into the blood.
a. How would the partial pressure of oxygen in the blood change?
Problem 59b
In certain lung ailments such as emphysema, there is a decrease in the ability of oxygen to diffuse into the blood.
b. Why does a person with severe emphysema sometimes use a portable oxygen tank?
Problem 62
Using the answer from problem 8.61, how many grams of nitrogen are in Whitney's lungs at STP if air contains 78% nitrogen?
Problem 64b
Two flasks of equal volume and at the same temperature contain different gases. One flask contains 5.0 g of O2 and the other flask contains 5.0 g of H2. Is each of the following statements true or false? Explain.
b. The pressures in the flasks are the same.
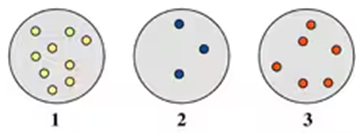
Problem 65b
At 100 °C, which of the following diagrams (1, 2, or 3) represents a gas sample that exerts the:
b. highest pressure?
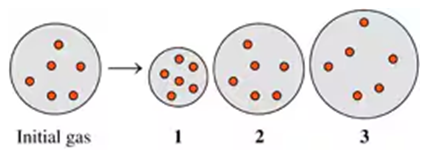
Problem 66c
Indicate which diagram (1, 2, or 3) represents the volume of the gas sample in a flexible container when each of the following changes (a to d) takes place:
c. Atmospheric pressure decreases if temperature does not change.
Problem 66d
Indicate which diagram (1, 2, or 3) represents the volume of the gas sample in a flexible container when each of the following changes (a to d) takes place:
d. Doubling the atmospheric pressure and doubling the Kelvin temperature.
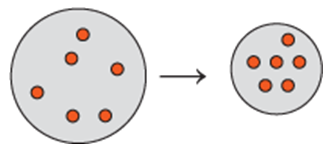
Problem 67c
A balloon is filled with helium gas with a partial pressure of 1.00 atm and neon gas with a partial pressure of 0.50 atm. For each of the following changes (a to e) of the initial balloon, select the diagram (A, B, or C) that shows the final volume of the balloon:
<IMAGE>
c. All of the neon gas is removed (T and P do not change).
Problem 67d
A balloon is filled with helium gas with a partial pressure of 1.00 atm and neon gas with a partial pressure of 0.50 atm. For each of the following changes (a to e) of the initial balloon, select the diagram (A, B, or C) that shows the final volume of the balloon:
<IMAGE>
d. The Kelvin temperature doubles and half of the gas atoms leak out (P does not change).
Problem 68a
Indicate if pressure increases, decreases, or stays the same in each of the following:
a.
Problem 69b
At a restaurant, a customer chokes on a piece of food. You put your arms around the person's waist and use your fists to push up on the person's abdomen, an action called the Heimlich maneuver.
b. Why does it cause the person to expel the food item from the airway?
Problem 71
In 1783, Jacques Charles launched his first balloon filled with hydrogen gas, which he chose because it was lighter than air. If the balloon had a volume of 31 000 L, how many kilograms of hydrogen were needed to fill the balloon at STP?
<IMAGE>
Problem 77b
A weather balloon is partially filled with helium to allow for expansion at high altitudes. At STP, a weather balloon is filled with enough helium to give a volume of 25.0 L. At an altitude of 30.0 km and –35 ⁰C, it has expanded to 2460 L. The increase in volume causes it to burst and a small parachute returns the instruments to Earth.
b. What is the final pressure, in millimeters of mercury, of the helium inside the balloon when it bursts?
Problem 78a
A mixture of nitrogen (N2) and helium has a volume of 250 mL at 30 °C and a total pressure of 745 mmHg.
a. If the partial pressure of helium is 32 mmHg, what is the partial pressure of the nitrogen?
Problem 80
What is the total pressure, in millimeters of mercury, of a gas mixture containing argon gas at 0.25 atm, helium gas at 350 mmHg, and nitrogen gas at 360 Torr?