Suppose crossover occurs between the homologous chromosomes in the previous problem. At what stage of M phase do alleles D and d segregate?
Ch. 3 - Cell Division and Chromosome Heredity

Sanders3rd EditionGenetic Analysis: An Integrated ApproachISBN: 9780135564172Not the one you use?Change textbook
Chapter 3, Problem 11a
Describe the role of the following structures or proteins in cell division:
Microtubules
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Microtubules are dynamic structures composed of tubulin proteins that play a critical role in cell division, particularly during mitosis and meiosis.
During prophase, microtubules form the mitotic spindle, which is essential for organizing and segregating chromosomes.
In metaphase, microtubules attach to the kinetochores of chromosomes and align them at the metaphase plate, ensuring proper chromosome positioning.
During anaphase, microtubules shorten, pulling sister chromatids apart toward opposite poles of the cell, ensuring equal distribution of genetic material.
Microtubules also contribute to cytokinesis by helping to position the cleavage furrow, which divides the cytoplasm into two daughter cells.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
2mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Microtubules
Microtubules are dynamic, tube-like structures made of tubulin protein subunits. They are a key component of the cytoskeleton and play a crucial role in maintaining cell shape, enabling intracellular transport, and facilitating cell division. During mitosis, microtubules form the mitotic spindle, which helps segregate chromosomes into daughter cells.
Recommended video:
Guided course
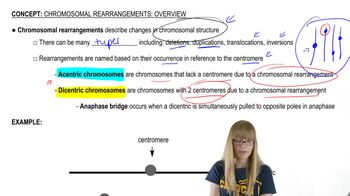
Rearrangement Overview
Mitotic Spindle
The mitotic spindle is a structure composed of microtubules that orchestrates the separation of chromosomes during cell division. It forms during prophase and is responsible for attaching to chromosomes at their kinetochores, ensuring that each daughter cell receives an identical set of chromosomes. Proper spindle function is essential for accurate cell division and genetic stability.
Recommended video:
Guided course
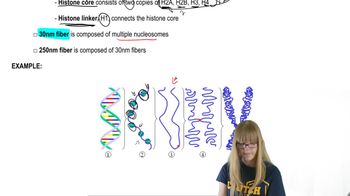
Chromosome Structure
Kinetochore
The kinetochore is a protein complex that assembles on the centromere of a chromosome during cell division. It serves as the attachment point for microtubules of the mitotic spindle, facilitating the movement of chromosomes. The interaction between kinetochores and microtubules is critical for the proper alignment and segregation of chromosomes, preventing errors that could lead to aneuploidy.
Recommended video:
Guided course
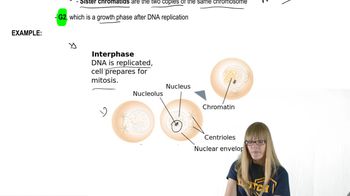
Mitosis Steps
Related Practice
Textbook Question
Textbook Question
Alleles A and a are on one pair of autosomes, and alleles B and b are on a separate pair of autosomes. Does crossover between one pair of homologs affect the expected proportions of gamete genotypes? Why or why not? Does crossover between both pairs of chromosomes affect the expected gamete proportions? Why or why not?
Textbook Question
How many Barr bodies are found in a normal human female nucleus? In a normal male nucleus?
3
views
Textbook Question
Describe the role of the following structures or proteins in cell division:
Cohesin protein
4
views
Textbook Question
Describe the role of the following structures or proteins in cell division:
Kinetochores
1
views
Textbook Question
Describe the role of the following structures or proteins in cell division:
Synaptonemal complex
1
views
