Back
BackProblem 1a
Compare and contrast the following terms:
Dominant and Recessive
Problem 1b
Compare and contrast the following terms:
Genotype and Phenotype
Problem 1c
Compare and contrast the following terms:
Homozygous and Heterozygous
Problem 1d
Compare and contrast the following terms:
Monohybrid cross and Test cross
Problem 1e
Compare and contrast the following terms:
Dihybrid cross and Trihybrid cross
Problem 2
For the cross BB×Bb, what is the expected genotype ratio? What is the expected phenotype ratio?
Problem 3
For the cross Aabb × aaBb, what is the expected genotype ratio? What is the expected phenotype ratio?
Problem 4
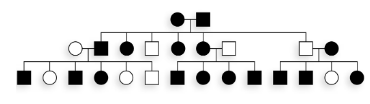
In mice, black coat color is dominant to white coat color. In the pedigree shown here, mice with a black coat are represented by darkened symbols, and those with white coats are shown as open symbols. Using allele symbols B and b, determine the genotypes for each mouse.
Problem A.4
A man, J.B., has a sister with autosomal recessive galactosemia (OMIM 230400), and his partner, S.B., has a brother with galactosemia. Galactosemia is a serious condition caused by an enzyme deficiency that prevents the metabolism of the sugar galactose. Neither J.B. nor S.B. has galactosemia, but they are concerned about the risk that a future child of theirs will have the condition. What is the probability their first child will have galactosemia?
Problem 5
Two parents plan to have three children. What is the probability that the children will be two girls and one boy?
Problem A.5
A woman, S.R., had a maternal grandfather with hemophilia A (OMIM 306700), an X-linked recessive condition that reduces blood clotting. S.R.'s maternal grandmother and paternal grandparents are free of the condition, as are her partner, his parents, and his grandparents. S.R. has no siblings. She wants to know the chance that a son of hers will have the condition. What is that probability?
Problem A.6
A 40-year-old woman whose father had Huntington disease currently shows no symptoms of the disease. She is newly pregnant with her first child and seeks your best estimate of the chance her child will inherit the disease. What is your estimate and how did you arrive at it? (Hint: See Figure 4.11)
Problem 6a
Consider the cross AaBbCC × AABbCc.
How many different gamete genotypes can each organism produce?
Problem 6b
Consider the cross AaBbCC × AABbCc.
Use a Punnett square to predict the expected ratio of offspring phenotypes.
Problem 6c
Consider the cross AaBbCC × AABbCc.
Use the forked-line method to predict the expected ratio of offspring phenotypes.
Problem 7a
If a chi-square test produces a chi-square value of 7.83 with 4 degrees of freedom,
In what interval range does the P value fall?
Problem 7b
If a chi-square test produces a chi-square value of 7.83 with 4 degrees of freedom,
Is the result sufficient to reject the chance hypothesis?
Problem 7c
If a chi-square test produces a chi-square value of 7.83 with 4 degrees of freedom,
Above what chi-square value would you reject the chance hypothesis for an experiment with 7 degrees of freedom?
Problem 8a
Determine whether the statements below are true or false. If a statement is false, provide the correct information or revise the statement to make it correct.
If a dihybrid cross is performed, the expected genotypic ratio is 9:3:3:1.
Problem 8b
Determine whether the statements below are true or false. If a statement is false, provide the correct information or revise the statement to make it correct.
A student uses the product rule to predict that the probability of flipping a coin twice and getting a head and then a tail is 1/4.
Problem 8c
Determine whether the statements below are true or false. If a statement is false, provide the correct information or revise the statement to make it correct.
A test cross between a heterozygous parent and a homozygous recessive parent is expected to produce a 1:1 genotypic and phenotypic ratio.
Problem 8d
Determine whether the statements below are true or false. If a statement is false, provide the correct information or revise the statement to make it correct.
The outcome of a trihybrid cross is predicted by the law of segregation.
Problem 8e
Determine whether the statements below are true or false. If a statement is false, provide the correct information or revise the statement to make it correct.
Reciprocal crosses that produce identical results demonstrate that a strain is pure-breeding.
Problem 8f
Determine whether the statements below are true or false. If a statement is false, provide the correct information or revise the statement to make it correct.
If a woman is heterozygous for albinism, an autosomal recessive condition that results in the absence of skin pigment, the proportion of her gametes carrying the allele that allows pigment expression is expected to be 75%.
Problem 8g
Determine whether the statements below are true or false. If a statement is false, provide the correct information or revise the statement to make it correct.
The progeny of a trihybrid cross are expected to have one of 27 different genotypes.
Problem 8h
Determine whether the statements below are true or false. If a statement is false, provide the correct information or revise the statement to make it correct.
If a dihybrid plant is self-fertilized,
(1) 9/16 of the progeny will have the same phenotype as the F₁ parent.
(2) 1/16 of the progeny will be true-breeding.
(3) 1/2 of the progeny will be heterozygous at one or both loci.
Problem 9a
In the datura plant, purple flower color is controlled by a dominant allele, P. White flowers are found in plants homozygous for the recessive allele p. Suppose that a purple-flowered datura plant with an unknown genotype is self-fertilized and that its progeny are 28 purple-flowered plants and 10 white-flowered plants.
Use the results of the self-fertilization to determine the genotype of the original purple-flowered plant.
Problem 9b
In the datura plant, purple flower color is controlled by a dominant allele, P. White flowers are found in plants homozygous for the recessive allele p. Suppose that a purple-flowered datura plant with an unknown genotype is self-fertilized and that its progeny are 28 purple-flowered plants and 10 white-flowered plants.
If one of the purple-flowered progeny plants is selected at random and self-fertilized, what is the probability it will breed true?
Problem 10a
The dorsal pigment pattern of frogs can be either 'leopard' (white pigment between dark spots) or 'mottled' (pigment between spots appears mottled). The trait is controlled by an autosomal gene. Males and females are selected from pure-breeding populations, and a pair of reciprocal crosses is performed. The cross results are shown below.
Cross 1: P₁: Male leopard x male mottled
F₁: All mottled
F₂: 70 mottled, 22 leopard
Cross 2: P₁: Male mottled x female leopard
F₁: All mottled
F₂: 50 mottled, 18 leopard
Which of the phenotypes is dominant? Explain your answer.
Problem 10b
The dorsal pigment pattern of frogs can be either 'leopard' (white pigment between dark spots) or 'mottled' (pigment between spots appears mottled). The trait is controlled by an autosomal gene. Males and females are selected from pure-breeding populations, and a pair of reciprocal crosses is performed. The cross results are shown below.
Cross 1: P₁: Male leopard x male mottled
F₁: All mottled
F₂: 70 mottled, 22 leopard
Cross 2: P₁: Male mottled x female leopard
F₁: All mottled
F₂: 50 mottled, 18 leopard
Compare and contrast the results of the reciprocal crosses in the context of autosomal gene inheritance.