Alleles A and a are on one pair of autosomes, and alleles B and b are on a separate pair of autosomes. Does crossover between one pair of homologs affect the expected proportions of gamete genotypes? Why or why not? Does crossover between both pairs of chromosomes affect the expected gamete proportions? Why or why not?
Ch. 3 - Cell Division and Chromosome Heredity

Sanders3rd EditionGenetic Analysis: An Integrated ApproachISBN: 9780135564172Not the one you use?Change textbook
Chapter 3, Problem 11b
Describe the role of the following structures or proteins in cell division:
Cohesin protein
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Understand that cohesin is a protein complex that plays a critical role in cell division by ensuring sister chromatids remain attached to each other after DNA replication.
Learn that cohesin forms a ring-like structure around sister chromatids, physically holding them together to maintain their alignment during the early stages of mitosis and meiosis.
Recognize that cohesin is essential for proper chromosome segregation, as it prevents premature separation of sister chromatids, which could lead to aneuploidy or other genetic errors.
Explore how cohesin is regulated during cell division: it is cleaved by the enzyme separase during anaphase, allowing sister chromatids to separate and move to opposite poles of the cell.
Understand the broader significance of cohesin in maintaining genomic stability and its involvement in certain genetic disorders when its function is impaired.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
2mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Cohesin Protein
Cohesin is a protein complex that plays a crucial role in holding sister chromatids together after DNA replication. It forms a ring-like structure that encircles the chromatids, ensuring they remain attached until the appropriate stage of cell division. This attachment is vital for accurate chromosome segregation during mitosis and meiosis, preventing aneuploidy.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Proteins
Cell Division
Cell division is the process by which a parent cell divides into two or more daughter cells. It encompasses two main types: mitosis, which results in two genetically identical cells, and meiosis, which produces gametes with half the genetic material. Proper regulation of cell division is essential for growth, development, and tissue repair.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Cell-cell interactions
Chromosome Segregation
Chromosome segregation is the process during cell division where replicated chromosomes are separated and distributed into daughter cells. This process is critical for maintaining genetic stability, as each daughter cell must receive an accurate copy of the genetic material. Cohesin proteins are integral to this process, as they ensure that sister chromatids are held together until the right moment for separation.
Recommended video:
Guided course
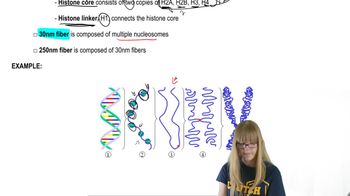
Chromosome Structure
Related Practice
Textbook Question
Textbook Question
How many Barr bodies are found in a normal human female nucleus? In a normal male nucleus?
3
views
Textbook Question
Describe the role of the following structures or proteins in cell division:
Microtubules
2
views
Textbook Question
Describe the role of the following structures or proteins in cell division:
Kinetochores
1
views
Textbook Question
Describe the role of the following structures or proteins in cell division:
Synaptonemal complex
1
views
Textbook Question
A woman's father has ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency (OTD), an X-linked recessive disorder producing mental deterioration if not properly treated. The woman's mother is homozygous for the wild-type allele.
What is the woman's genotype? (Use D to represent the dominant allele and d to represent the recessive allele.)
