The results shown are from a DNA test for four genes used in a paternity identification case. DNA for the mother (M) and her child (C) are shown along with DNA from two possible fathers, F1 and F2. In the 'C' column, label the DNA bands contributed by the mother with 'M' and the DNA bands contributed by the father with 'F.'

Compare methods for constructing homologous recombinant transgenic mice and yeast.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
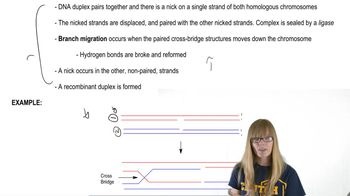
Homologous Recombination
Transgenic Organisms
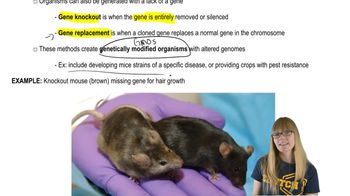
Gene Targeting Techniques

Using animal models of human diseases can lead to insights into the cellular and genetic bases of the diseases. Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) is the consequence of an X-linked recessive allele.
How would you make a mouse model of DMD?
Using animal models of human diseases can lead to insights into the cellular and genetic bases of the diseases. Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) is the consequence of an X-linked recessive allele.
How would you make a Drosophila model of DMD?
Figure E.1 illustrates the results of an electrophoretic analysis of 13 CODIS STR markers on a DNA sample and identifies the alleles for each gene. Table E.2 lists the frequencies for alleles of three of the STRs shown in the figure. Use this information to calculate the frequency of the genotype for STR genes FGA, vWA, and D3S1358 given in Figure E.1.
Additional STR allele frequency information can be added to improve the analysis in Problem 8. The frequency of D8S1179₁₂ = 0.12. The frequency of D16S539₁₈ = 0.08 and of D16S539₂₀ = 0.21. Lastly, D18S51₁₉ = 0.13 and D18S51₂₀ = 0.10. Combine the allele frequency information for these three STR genes with the information used in Problem 8 to calculate the frequency of the genotype for six of the STR genes.
