 Back
BackProblem 29b
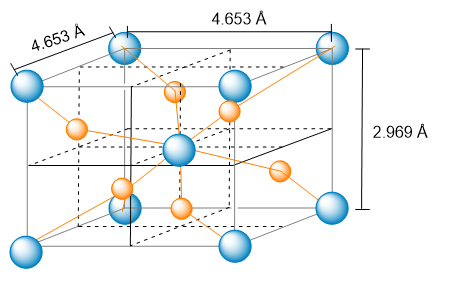
The unit cell of nickel arsenide is shown here. (b) What is the empirical formula?
Problem 30a
The unit cell of a compound containing potassium, aluminum, and fluorine is shown here. (a) What type of lattice does this crystal possess (all three lattice vectors are mutually perpendicular)?

- For each of these solids, state whether you would expect it to possess metallic properties: (a) TiCl4 (b) NiCo alloy (c) W (d) Ge (e) ScN
Problem 32
Problem 33a
Consider the unit cells shown here for three different structures that are commonly observed for metallic elements. (a) Which structure(s) corresponds to the densest packing of atoms?

Problem 33b
Consider the unit cells shown here for three different structures that are commonly observed for metallic elements. (b) Which structure(s) corresponds to the least dense packing of atoms?

Problem 34
Sodium metal (atomic weight 22.99 g/mol) adopts a body-centered cubic structure with a density of 0.97 g/cm3. (a) Use this information and Avogadro’s number (NA = 6.022 × 1023/mol) to estimate the atomic radius of sodium. (b) If sodium didn't react so vigorously, it could float on water. Use the answer from part (a) to estimate the density of Na if its structure were that of a cubic close-packed metal. Would it still float on water?
- Iridium crystallizes in a face-centered cubic unit cell that has an edge length of 3.833 Å. (a) Calculate the atomic radius of an iridium atom. (b) Calculate the density of iridium metal.
Problem 35
Problem 36a
Calcium crystallizes in a body-centered cubic structure at 467°C. (a) How many Ca atoms are contained in each unit cell?
Problem 36b,c,d
Calcium crystallizes in a body-centered cubic structure at 467°C. (b) How many nearest neighbors does each Ca atom possess? (c) Estimate the length of the unit cell edge, a, from the atomic radius of calcium (1.97 Å). (d) Estimate the density of Ca metal at this temperature.
Problem 37
Calcium crystallizes in a face-centered cubic unit cell at room temperature that has an edge length of 5.588 Å.
a. Calculate the atomic radius of a calcium atom.
b. Calculate the density of Ca metal at this temperature.
- Calculate the volume in ų of a face-centered cubic unit cell if it is composed of atoms with an atomic radius of 1.82 Å.
Problem 38
- Aluminum metal crystallizes in a face-centered cubic unit cell. (a) How many aluminum atoms are in a unit cell? (b) Estimate the length of the unit cell edge, a, from the atomic radius of aluminum (1.43 Å). (c) Calculate the density of aluminum metal.
Problem 39
Problem 40
An element crystallizes in a face-centered cubic lattice. The edge of the unit cell is 4.078 Å, and the density of the crystal is 19.30 g>cm3. Calculate the atomic weight of the element and identify the element.
Problem 41
Which of these statements about alloys and intermetallic compounds is false? (a) Bronze is an example of an alloy. (b) 'Alloy' is just another word for 'a chemical compound of fixed composition that is made of two or more metals.' (c) Intermetallics are compounds of two or more metals that have a definite composition and are not considered alloys. (d) If you mix two metals together and, at the atomic level, they separate into two or more different compositional phases, you have created a heterogeneous alloy. (e) Alloys can be formed even if the atoms that comprise them are rather different in size.
Problem 42b
Determine if each statement is true or false: (b) Substitutional alloys have 'solute' atoms that replace 'solvent' atoms in a lattice, but interstitial alloys have 'solute' atoms that are in between the 'solvent' atoms in a lattice.
Problem 43
For each of the following alloy compositions, indicate whether you would expect it to be a substitutional alloy, an interstitial alloy, or an intermetallic compound: (a) Fe0.97Si0.03 (b) Fe0.60Ni0.40 (c) SmCo5.
- For each of the following alloy compositions, indicate whether you would expect it to be a substitutional alloy, an interstitial alloy, or an intermetallic compound: (a) Cu₀.₆₆Zn₀.₃₄ (b) Ag₃Sn (c) Ti₀.₉₉O₀.₀₁.
Problem 44
Problem 45c
Indicate whether each statement is true or false: (c) Nonmetallic elements are never found in alloys.
- Indicate whether each statement is true or false: (a) Intermetallic compounds have a fixed composition. (b) Copper is the majority component in both brass and bronze. (c) In stainless steel, the chromium atoms occupy interstitial positions.
Problem 46
Problem 48
An increase in temperature causes most metals to undergo thermal expansion, which means the volume of the metal increases upon heating. How does thermal expansion affect the unit cell length? What is the effect of an increase in temperature on the density of a metal?
Problem 49b
State whether each sentence is true or false: (b) Metals have high electrical conductivities because they are denser than other solids.
Problem 51a
The molecular-orbital diagrams for two- and four-atom linear chains of lithium atoms are shown in Figure 12.21. Construct a molecular-orbital diagram for a chain containing six lithium atoms and use it to answer the following questions: a. How many molecular orbitals are there in the diagram?
Problem 51c
The molecular-orbital diagrams for two- and four-atom linear chains of lithium atoms are shown in Figure 12.21. Construct a molecular-orbital diagram for a chain containing six lithium atoms and use it to answer the following questions: c. How many nodes are in the highest-energy molecular orbital?
Problem 51e
The molecular-orbital diagrams for two- and four-atom linear chains of lithium atoms are shown in Figure 12.21. Construct a molecular-orbital diagram for a chain containing six lithium atoms and use it to answer the following questions: e. How many nodes are in the lowest-energy unoccupied molecular orbital (LUMO)?
Problem 52f
Repeat Exercise 12.51 for a linear chain of eight lithium atoms. (f) How does the HOMO–LUMO energy gap for this case compare to that of the four-atom case?
Problem 53a
Which would you expect to be the more ductile element: a. Ag or Mo
Problem 54
Which of the following statements does not follow from the fact that the alkali metals have relatively weak metal–metal bonding? (a) The alkali metals are less dense than other metals. (b) The alkali metals are soft enough to be cut with a knife. (c) The alkali metals are more reactive than other metals. (d) The alkali metals have higher melting points than other metals. (e) The alkali metals have low ionization energies.
Problem 57a
Tausonite, a mineral composed of Sr, O, and Ti, has the cubic unit cell shown in the drawing. (a) What is the empirical formula of this mineral?

Problem 58
The unit cell of a compound containing Co and O has a unit cell shown in the diagram. The Co atoms are on the corners, and the O atoms are completely within the unit cell. a. What is the empirical formula of this compound? b. What is the oxidation state of the metal?
- Alabandite is a mineral composed of manganese(II) sulfide (MnS). The mineral adopts the rock salt structure. The length of an edge of the MnS unit cell is 5.223 Å at 25 °C. Determine the density of MnS in g/cm³.
Problem 59
