Textbook Question
What is the minimum number of atoms that could be contained in the unit cell of an element with a face-centered cubic lattice? (a) 1, (b) 2, (c) 3, (d) 4, (e) 5.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
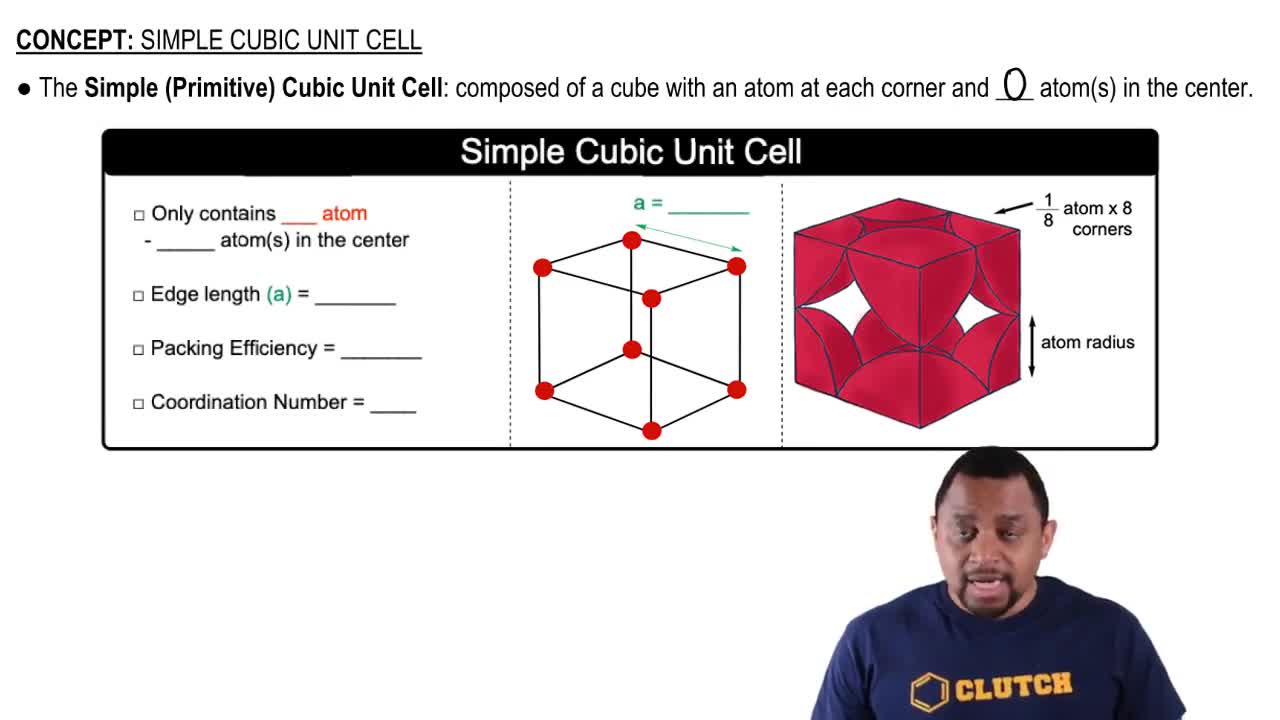

What is the minimum number of atoms that could be contained in the unit cell of an element with a face-centered cubic lattice? (a) 1, (b) 2, (c) 3, (d) 4, (e) 5.
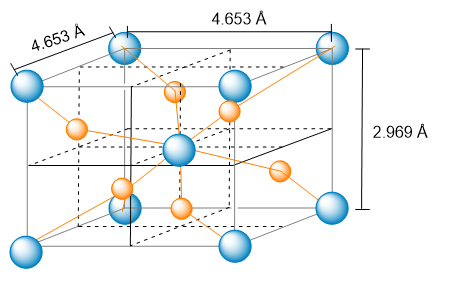
The unit cell of a compound containing potassium, aluminum, and fluorine is shown here. (a) What type of lattice does this crystal possess (all three lattice vectors are mutually perpendicular)?
Consider the unit cells shown here for three different structures that are commonly observed for metallic elements. (a) Which structure(s) corresponds to the densest packing of atoms?