Back
BackProblem 51
Use the Binomial Theorem to expand each expression and write the result in simplified form. (x1/3 +x-1/3)3
Problem 53
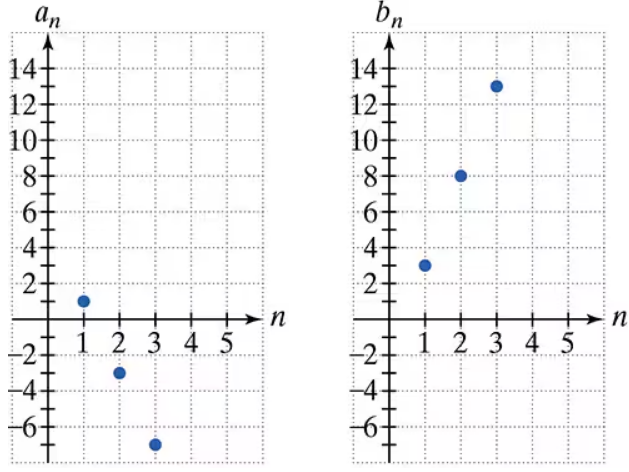
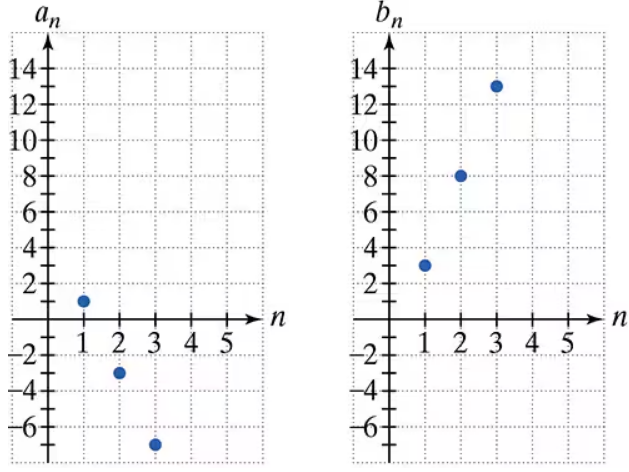
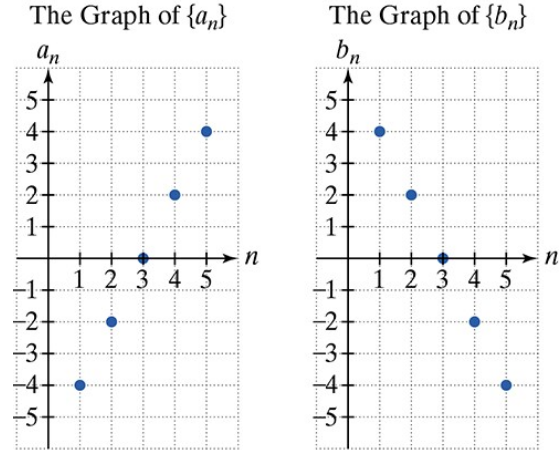
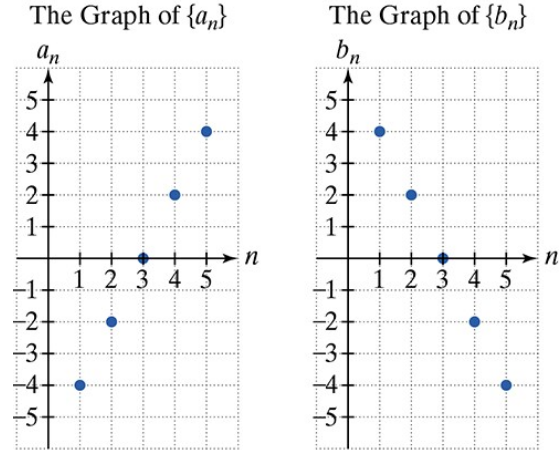
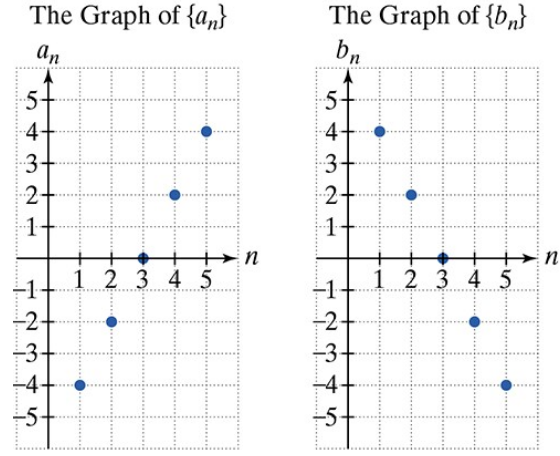
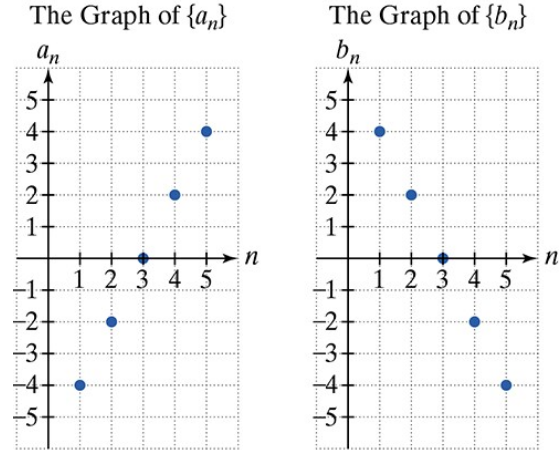
Use the graphs of the arithmetic sequences {a} and {b} to solve Exercises 51-58. If {an} is a finite sequence whose last term is -83, how many terms does {an} contain?
Problem 53
In Exercises 51–56, the general term of a sequence is given. Determine whether the sequence is arithmetic, geometric, or neither. If the sequence is arithmetic, find the common difference; if it is geometric, find the common ratio. an = 2n
Problem 53
Use the formula for nCr to solve Exercises 49–56. You volunteer to help drive children at a charity event to the zoo, but you can fit only 8 of the 17 children present in your van. How many different groups of 8 children can you drive?
Problem 53
Find f(x + h) − f(x)/h and simplify. f(x) = x4+7
Problem 53
In Exercises 43–54, express each sum using summation notation. Use 1 as the lower limit of summation and i for the index of summation. 1+3+5+⋯+ (2n−1)
Problem 53
If you toss a fair coin six times, what is the probability of getting all heads?
Problem 55
Use the formula for nCr to solve Exercises 49–56. To win at LOTTO in the state of Florida, one must correctly select 6 numbers from a collection of 53 numbers (1 through 53). The order in which the selection is made does not matter. How many different selections are possible?
Problem 55
In Exercises 55–60, express each sum using summation notation. Use a lower limit of summation of your choice and k for the index of summation. 5+7+9+11+⋯+ 31
Problem 55
Use the graphs of the arithmetic sequences {a} and {b} to solve Exercises 51-58. Find the difference between the sum of the first 14 terms of {bn} and the sum of the first 14 terms of {an}.
Problem 55
Find the middle term in the expansion of (3/x + x/3)10
Problem 55
The general term of a sequence is given. Determine whether the sequence is arithmetic, geometric, or neither. If the sequence is arithmetic, find the common difference; if it is geometric, find the common ratio. an = n2 + 5
Problem 57
Let {an} = - 5, 10, - 20, 40, ..., {bn} = 10, - 5, - 20, - 35, ..., {cn} = - 2, 1, - 1/2, 1/4 Find a10 + b10.
Problem 57
Express each sum using summation notation. Use a lower limit of summation of your choice and k for the index of summation. a+ar+ar2+⋯+ ar12
Problem 57
Use mathematical induction to prove that the statement is true for every positive integer n. 5 + 10 + 15 + ... + 5n = (5n(n+1))/2
Problem 58
Use mathematical induction to prove that the statement is true for every positive integer n. 1 + 4 + 4^2 + ... + 4^(n-1) = ((4^n)-1)/3
Problem 59
In Exercises 55–60, express each sum using summation notation. Use a lower limit of summation of your choice and k for the index of summation.
Problem 59
Let {an} = - 5, 10, - 20, 40, ..., {bn} = 10, - 5, - 20, - 35, ..., {cn} = - 2, 1, - 1/2, 1/4 Find the difference between the sum of the first 10 terms of {an} and the sum of the first 10 terms of {bn}.
Problem 61
Let {an} = - 5, 10, - 20, 40, ..., {bn} = 10, - 5, - 20, - 35, ..., {cn} = - 2, 1, - 1/2, 1/4 Find the difference between the sum of the first 6 terms of {an} and the sum of the infinite seris containing all the terms of {cn}.
Problem 61
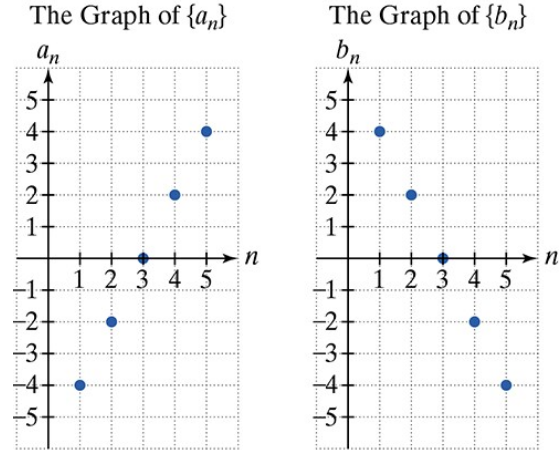
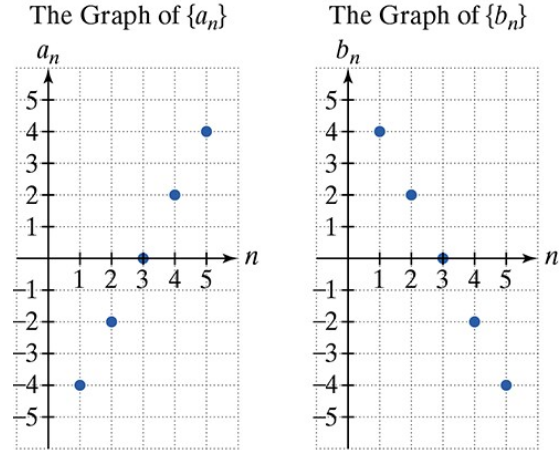
In Exercises 61–68, use the graphs of and to find each indicated sum.
Problem 62
Evaluate the given binomial coefficient 11 8
Problem 63
In Exercises 61–68, use the graphs of and to find each indicated sum.
Problem 63
Find a2 and a3 for each geometric sequence. 8, a2, a3, 27
Problem 64
Find a2 and a3 for each geometric sequence. 2, a2, a3, - 54
Problem 64
Use the Binomial Theorem to expand the binomial and express the result in simplified form. (2x+1)^3
Problem 64
In Exercises 61–68, use the graphs of and to find each indicated sum.
Problem 65
In Exercises 61–68, use the graphs of and to find each indicated sum.
Problem 65
Use the Binomial Theorem to expand the binomial and express the result in simplified form. ((x^2)-1)^4
Problem 66
In Exercises 61–68, use the graphs of and to find each indicated sum.
Problem 67
In Exercises 61–68, use the graphs of and to find each indicated sum.