Back
BackProblem 41
Find the sum of the first 15 terms of the geometric sequence: 5, -15, 45, -135
Problem 43
Find the sum of each infinite geometric series.
Problem 43
Express each sum using summation notation. Use 1 as the lower limit of summation and i for the index of summation.
Problem 43
Find the term indicated in each expansion. (x2 + y3)8; sixth term
Problem 43
Use the formula for the sum of the first n terms of a geometric sequence to find the indicated sum.
Problem 43
Find the sum of the even integers between 21 and 45.
Problem 44
Find the sum of the odd integers between 30 and 54.
Problem 45
Write out the first three terms and the last term. Then use the formula for the sum of the first n terms of an arithmetic sequence to find the indicated sum.
Problem 45
In Exercises 45-46, it is equally probable that the pointer on the spinner shown will land on any one of the eight regions, numbered 1 through 8. If the pointer lands on a borderline, spin again. Find the probability that the pointer will stop on an odd number or a number less than 6.

Problem 45
Express each repeating decimal as a fraction in lowest terms.
Problem 45
Express each sum using summation notation. Use as the lower limit of summation and for the index of summation.
Problem 45
Find the term indicated in each expansion. (x − 1/2)9; fourth term
Problem 47
Find the term indicated in each expansion. (x2 + y)22; the term containing y14
Problem 47
Write out the first three terms and the last term. Then use the formula for the sum of the first n terms of an arithmetic sequence to find the indicated sum.
Problem 47
Find the sum of each infinite geometric series. 2 - 1 + 1/2 - 1/4 + ...
Problem 47
Express each sum using summation notation. Use 1 as the lower limit of summation and i for the index of summation. 1+2+3+⋯+ 30
Problem 47
Express each repeating decimal as a fraction in lowest terms.
Problem 48
Find the sum of each infinite geometric series. -6 + 4 - 8/3 + 16/9 - ...
Problem 49
Express each repeating decimal as a fraction in lowest terms.
Problem 49
Write out the first three terms and the last term. Then use the formula for the sum of the first n terms of an arithmetic sequence to find the indicated sum.
Problem 49
Use the formula for nCr to solve Exercises 49–56. An election ballot asks voters to select three city commissioners from a group of six candidates. In how many ways can this be done?
Problem 49
Express each sum using summation notation. Use 1 as the lower limit of summation and i for the index of summation. 1/2+2/3+3/4+⋯+ 14/(14+1)
Problem 49
In Exercises 49–52, a single die is rolled twice. Find the probability of rolling a 2 the first time and a 3 the second time.
Problem 49
Use the Binomial Theorem to expand each expression and write the result in simplified form. (x3 +x-2)4
Problem 50
Express each repeating decimal as a fraction in lowest terms. 0.6 (repeating 6)
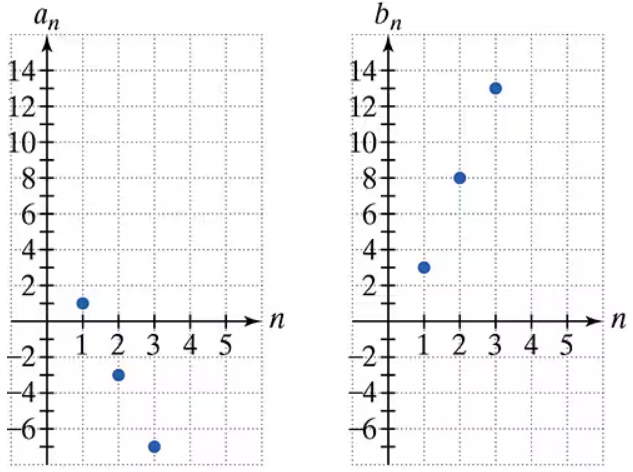
Problem 51
Use the graphs of the arithmetic sequences {a} and {b} to solve Exercises 51-58.
Find a14+b12.
Problem 51
Express each sum using summation notation. Use as the lower limit of summation and for the index of summation.
Problem 51
In Exercises 49–52, a single die is rolled twice. Find the probability of rolling an even number the first time and a number greater than 2 the second time.
Problem 51
The general term of a sequence is given. Determine whether the sequence is arithmetic, geometric, or neither. If the sequence is arithmetic, find the common difference; if it is geometric, find the common ratio. an = n + 5
Problem 51
Use the formula for nCr to solve Exercises 49–56. Of 12 possible books, you plan to take 4 with you on vacation. How many different collections of 4 books can you take?