Back
BackProblem 68
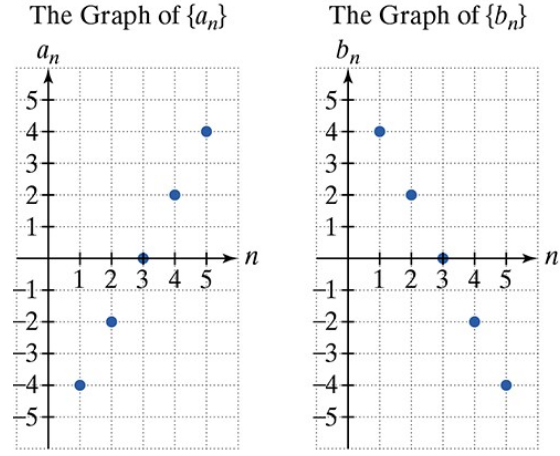
In Exercises 61–68, use the graphs of and to find each indicated sum.
Problem 69
Write the first three terms in the binomial expansion, expressing the result in simplified form. (x-3)^9
Problem 71
Find the term indicated in the expansion. (2x-3)^6; fifth term
Problem 72
Evaluate the expression. *permutation notation* the number of permutations 8 things taken 3 at a time (sub 8)P(sub 3)
Problem 73
Evaluate the expression. *permutation notation* the number of permutations 9 things taken 5 at a time (sub 9)P(sub 5)
Problem 76
After a 20% reduction, a 42-inch HDTV sold for $256. What was the price before the reduction?
Problem 78
A club with 15 members is to choose four officers–president, vice president, secretary, and treasurer. In how many ways can these offices be filled?
Problem 79
How many different ways can a director select 4 actors from a group of 20 actors to attend a workshop on performing in rock musicals?
Problem 81
Use the Binomial Theorem to expand and then simplify the result: (x2 +x+ 1)3.
Problem 81
In Exercises 81–85, use a calculator's factorial key to evaluate each expression.
Problem 82
Use a calculator's factorial key to evaluate each expression. (300/20)!
Problem 82
In the sequence 21,700, 23,172, 24,644, 26,116,... which term is 314,628?
Problem 82
In how many ways can five airplanes line up for departure on a runway?
Problem 82
Find the term in the expansion of (x2 + y2)5 containing x4 as a factor.
Problem 83
In Exercises 81–85, use a calculator's factorial key to evaluate each expression.
Problem 84
Show that the sum of the first n positive odd integers,1 +3 +5 + ··· + (2n − 1), ... is n².
Problem 84
Use a calculator's factorial key to evaluate each expression. 20!/(20−3)!
Problem 85
Write an equation in point-slope form and slope-intercept form for the line passing through (-2, -6) and perpendicular to the line whose equation is x − 3y+ 9 = 0.
Problem 85
In Exercises 81–85, use a calculator's factorial key to evaluate each expression.
Problem 86
Solve: .
Problem 87
Solve: log2 (x+9) — log2 x = 1.
Problem 88
Graph: f(x) = -2(x − 1)² (x + 3).
Problem 88
Exercises 88–90 will help you prepare for the material covered in the next section. Consider the sequence 1, −2, 4, −8, 16, ………. Find a2/a3, a1/a2, a4/a3 and a5/a4 What do you observe?
Problem 89
Evaluate n!/(n-r)! for n = 20 and r = 3
Problem 89
Exercises 88–90 will help you prepare for the material covered in the next section. Consider the sequence whose nth term is an = (3)5n Find a2/a3, a1/a2, a4/a3 and a5/a4 What do you observe?
Problem 89
A die is rolled. Find the probability of getting a number less than 5.
Problem 90
A die is rolled. Find the probability of getting a number less than 3 or greater than 4.
Problem 90
Exercises 88–90 will help you prepare for the material covered in the next section. Use the formula an = a₁3(n-1) to find the seventh term of the sequence 11, 33, 99, 297,...
Problem 90
Evaluate n!/(n-r)!r! for n = 8 and r = 3
Problem 91
You are dealt one card from a 52-card deck. Find the probability of getting an ace or a king.