Back
BackProblem 37
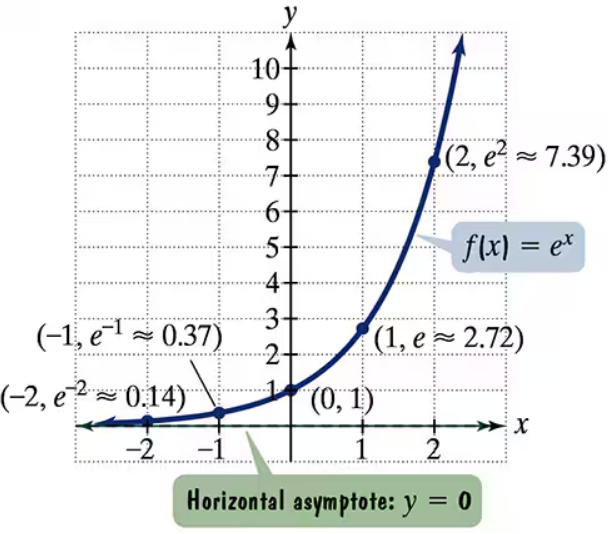
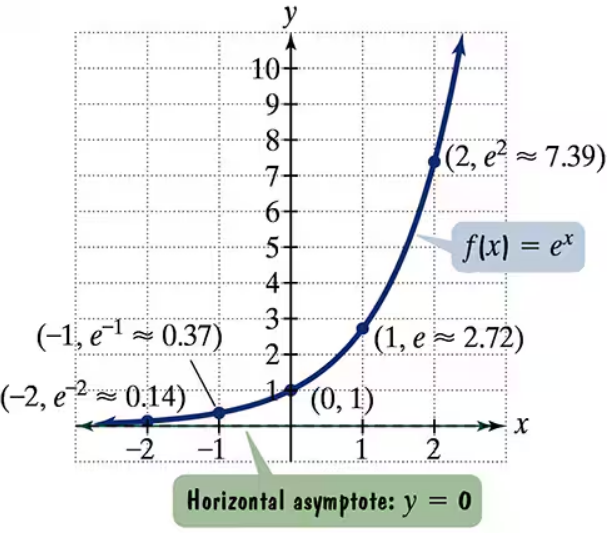
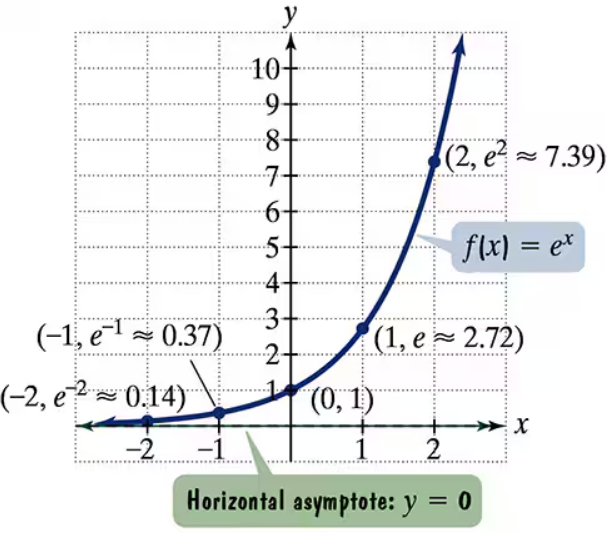
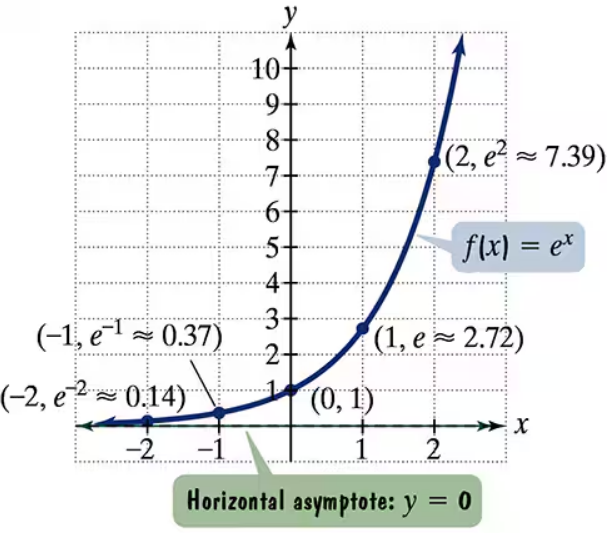
The figure shows the graph of f(x) = ex. In Exercises 35-46, use transformations of this graph to graph each function. Be sure to give equations of the asymptotes. Use the graphs to determine graphs. each function's domain and range. If applicable, use a graphing utility to confirm your hand-drawn g(x) = ex+2
Problem 37
Solve each exponential equation in Exercises 23–48. Express the solution set in terms of natural logarithms or common logarithms. Then use a calculator to obtain a decimal approximation, correct to two decimal places, for the solution. 7(x+2)=410
Problem 39
The figure shows the graph of f(x) = ex. In Exercises 35-46, use transformations of this graph to graph each function. Be sure to give equations of the asymptotes. Use the graphs to determine graphs. each function's domain and range. If applicable, use a graphing utility to confirm your hand-drawn h(x) = ex-1+2
Problem 39
Solve each exponential equation in Exercises 23–48. Express the solution set in terms of natural logarithms or common logarithms. Then use a calculator to obtain a decimal approximation, correct to two decimal places, for the solution. 70.3x=813
Problem 39
Use properties of logarithms to expand each logarithmic expression as much as possible. Where possible, evaluate logarithmic expressions without using a calculator.
Problem 39
In Exercises 39–40, graph f and g in the same rectangular coordinate system. Use transformations of the graph of f to obtain the graph of g. Graph and give equations of all asymptotes. Use the graphs to determine each function's domain and range. f(x) = log x and g(x) = - log (x+3)
Problem 39
Evaluate each expression without using a calculator. log5 57
Problem 40
In Exercises 39–40, graph f and g in the same rectangular coordinate system. Use transformations of the graph of f to obtain the graph of g. Graph and give equations of all asymptotes. Use the graphs to determine each function's domain and range. f(x) = ln x and g(x) = - ln (2x)




Problem 41
Use properties of logarithms to condense each logarithmic expression. Write the expression as a single logarithm whose coefficient is 1. Where possible, evaluate logarithmic expressions without using a calculator. log 5 + log 2
Problem 41
The figure shows the graph of f(x) = ex. In Exercises 35-46, use transformations of this graph to graph each function. Be sure to give equations of the asymptotes. Use the graphs to determine graphs. each function's domain and range. If applicable, use a graphing utility to confirm your hand-drawn h(x) = e-x
Problem 41
Evaluate each expression without using a calculator.
Problem 41
Solve each exponential equation in Exercises 23–48. Express the solution set in terms of natural logarithms or common logarithms. Then use a calculator to obtain a decimal approximation, correct to two decimal places, for the solution. 5(2x+3)=3(x−1)
Problem 43
Use properties of logarithms to condense each logarithmic expression. Write the expression as a single logarithm whose coefficient is 1. Where possible, evaluate logarithmic expressions without using a calculator. ln x + ln 7
Problem 43
Graph f(x) = 4x and g(x) = log4 x in the same rectangular coordinate system.
Problem 43
The figure shows the graph of f(x) = ex. In Exercises 35-46, use transformations of this graph to graph each function. Be sure to give equations of the asymptotes. Use the graphs to determine graphs. each function's domain and range. If applicable, use a graphing utility to confirm your hand-drawn g(x) = 2ex
Problem 43
Solve each exponential equation in Exercises 23–48. Express the solution set in terms of natural logarithms or common logarithms. Then use a calculator to obtain a decimal approximation, correct to two decimal places, for the solution. e2x−3ex+2=0
Problem 45
The figure shows the graph of f(x) = ex. In Exercises 35-46, use transformations of this graph to graph each function. Be sure to give equations of the asymptotes. Use the graphs to determine graphs. each function's domain and range. If applicable, use a graphing utility to confirm your hand-drawn h(x) = e2x + 1
Problem 45
Solve each exponential equation in Exercises 23–48. Express the solution set in terms of natural logarithms or common logarithms. Then use a calculator to obtain a decimal approximation, correct to two decimal places, for the solution. e4x+5e2x−24=0
Problem 45
Use properties of logarithms to condense each logarithmic expression. Write the expression as a single logarithm whose coefficient is 1. Where possible, evaluate logarithmic expressions without using a calculator. log2 (96) - log2 (3)
Problem 45
Graph f(x) = (1/2)x and g(x) = log1/2 x in the same rectangular coordinate system.
Problem 47
Graph functions f and g in the same rectangular coordinate system. Graph and give equations of all asymptotes. If applicable, use a graphing utility to confirm your hand-drawn graphs. f(x) = 3x and g(x) = 3-x
Problem 47
Solve each exponential equation in Exercises 23–48. Express the solution set in terms of natural logarithms or common logarithms. Then use a calculator to obtain a decimal approximation, correct to two decimal places, for the solution. 32x+3x−2=0
Problem 49
Solve each logarithmic equation in Exercises 49–92. Be sure to reject any value of x that is not in the domain of the original logarithmic expressions. Give the exact answer. Then, where necessary, use a calculator to obtain a decimal approximation, correct to two decimal places, for the solution. log3x=4
Problem 49
Use properties of logarithms to condense each logarithmic expression. Write the expression as a single logarithm whose coefficient is 1. Where possible, evaluate logarithmic expressions without using a calculator. log x + 3 log y
Problem 49
Graph functions f and g in the same rectangular coordinate system. Graph and give equations of all asymptotes. If applicable, use a graphing utility to confirm your hand-drawn graphs. f(x) = 3x and g(x) = (1/3). 3x
Problem 51
Solve each logarithmic equation in Exercises 49–92. Be sure to reject any value of x that is not in the domain of the original logarithmic expressions. Give the exact answer. Then, where necessary, use a calculator to obtain a decimal approximation, correct to two decimal places, for the solution. ln x=2
Problem 51
Graph functions f and g in the same rectangular coordinate system. Graph and give equations of all asymptotes. If applicable, use a graphing utility to confirm your hand-drawn graphs. f(x) = (½)x and g(x) = (½)x-1 + 1
Problem 51
In Exercises 50–53, use properties of logarithms to expand each logarithmic expression as much as possible. Where possible, evaluate logarithmic expressions without using a calculator.
Problem 51
Use properties of logarithms to condense each logarithmic expression. Write the expression as a single logarithm whose coefficient is 1. Where possible, evaluate logarithmic expressions without using a calculator. (1/2)ln x + ln y
Problem 53
Use properties of logarithms to condense each logarithmic expression. Write the expression as a single logarithm whose coefficient is 1. Where possible, evaluate logarithmic expressions without using a calculator. 2 logb x + 3 logb y