Back
BackProblem 1
Solve each system by the substitution method.
Problem 1
Determine whether the given ordered pair is a solution of the system.
Problem 1
Solve by the method of your choice. Identify systems with no solution and systems with infinitely many solutions, using set notation to express their solution sets.
Problem 1
Write the form of the partial fraction decomposition of the rational expression. It is not necessary to solve for the constants.(11x - 10)/(x − 2) (x + 1)
Problem 1
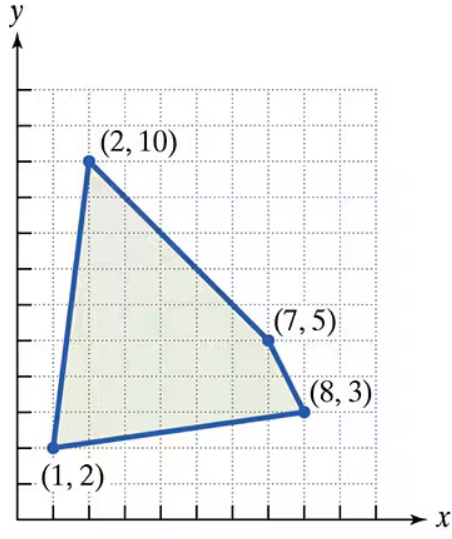
Find the value of the objective function at each corner of the graphed region. What is the maximum value of the objective function? What is the minimum value of the objective function? 1. Objective Function z=5x+6y
Problem 1
Determine if the given ordered triple is a solution of the system.
Problem 1
Ggraph each inequality. x+2y≤8
Problem 2
Solve by the method of your choice. Identify systems with no solution and systems with infinitely many solutions, using set notation to express their solution sets.
Problem 2
Determine whether the given ordered pair is a solution of the system.
Problem 3
Graph each inequality. x−2y>10
Problem 3
Find the value of the objective function at each corner of the graphed region. What is the maximum value of the objective function? What is the minimum value of the objective function? 1. Objective Function z=40x+50y
Problem 3
Determine if the given ordered triple is a solution of the system.
Problem 3
Write the form of the partial fraction decomposition of the rational expression. It is not necessary to solve for the constants.
Problem 3
In Exercises 1–4, determine whether the given ordered pair is a solution of the system. (2, 5) 2x + 3y = 17 x + 4y = 16

Problem 3
In Exercises 1–18, solve each system by the substitution method.
Problem 4
In Exercises 1–8, write the form of the partial fraction decomposition of the rational expression. It is not necessary to solve for the constants. (3x+16)/(x + 1) (x − 2)²
Problem 5
Graph each inequality. y≤(1/3)x
Problem 5
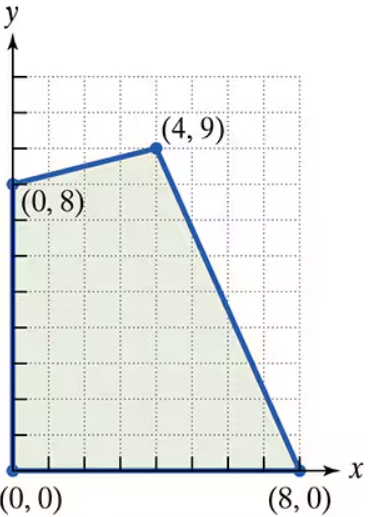
An objective function and a system of linear inequalities representing constraints are given. a. Graph the system of inequalities representing the constraints. b. Find the value of the objective function at each corner of the graphed region. c. Use the values in part (b) to determine the maximum value of the objective function and the values of x and y for which the maximum occurs.
Problem 5
In Exercises 5–18, solve each system by the substitution method. x + y = 4 y = 3x

Problem 5
Write the form of the partial fraction decomposition of the rational expression. It is not necessary to solve for the constants.
Problem 5
Solve each system in Exercises 5–18.
Problem 5
In Exercises 1–18, solve each system by the substitution method.
Problem 7
Write the form of the partial fraction decomposition of the rational expression. It is not necessary to solve for the constants.
Problem 7
A chemist needs to mix a solution that is 34% silver nitrate with one that is 4% silver nitrate to obtain 100 milliliters of a mixture that is 7% silver nitrate. How many milliliters of each of the solutions must be used?
Problem 7
Graph each inequality. y>2x−1
Problem 7
In Exercises 5–18, solve each system by the substitution method.
Problem 7
In Exercises 1–18, solve each system by the substitution method.
Problem 7
An objective function and a system of linear inequalities representing constraints are given. a. Graph the system of inequalities representing the constraints. b. Find the value of the objective function at each corner of the graphed region. c. Use the values in part (b) to determine the maximum value of the objective function and the values of x and y for which the maximum occurs.
Problem 7
Solve each system in Exercises 5–18.
Problem 8
In Exercises 1–8, write the form of the partial fraction decomposition of the rational expression. It is not necessary to solve for the constants. (7x2 -9x+3)/(x2+7)2