Where does the citric acid cycle occur in eukaryotes? a. in the cytosol of cells b. in the intermembrane space of mitochondria c. in the inner membrane of mitochondria d. in the matrix of mitochondria

Which of the following correctly describe the fermentation pathway? Select True or False for each statement.
T/FIt includes a reaction that oxidizes NADH to NAD+.
T/FIt synthesizes ATP by substrate-level phosphorylation.
T/FIt includes a reaction that reduces NAD+ to NADH.
T/FIt synthesizes electron acceptors, so that cellular respiration can continue.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
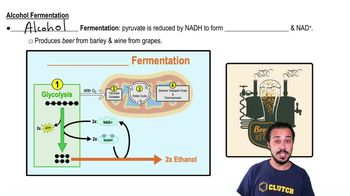
Fermentation Pathway
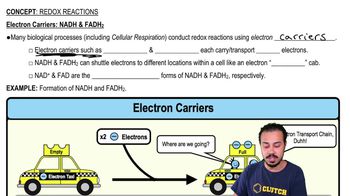
NAD+/NADH Cycle
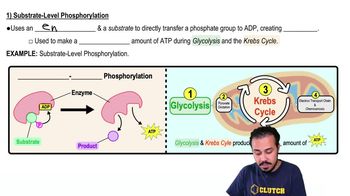
Substrate-Level Phosphorylation
What does the chemiosmotic hypothesis claim?
a. ATP is generated using phosphates taken from intermediates in the electron transport chain.
b. ATP is generated using a phosphate gradient produced by glycolysis and the citric acid cycle.
c. ATP is generated using a proton-motive force that is produced by the electron transport chain.
d. Water is generated using electrons taken from NADH and FADH2 and transported through the electron transport chain.
After glucose is fully oxidized by glycolysis, pyruvate processing, and the citric acid cycle, where is most of its energy stored?
Compare and contrast substrate-level phosphorylation and oxidative phosphorylation.
If you were to expose cells that are undergoing aerobic respiration to a radioactive oxygen isotope in the form of O2, which of the following molecules would you expect to be radiolabeled?
a. Pyruvate
b. Water
c. NADH
d. CO2
In step 3 of the citric acid cycle, the enzyme isocitrate dehydrogenase is regulated by NADH. Compare and contrast the regulation of this enzyme with the regulation of phosphofructokinase in glycolysis.
