Back
BackProblem 1
What is the main global reservoir of nitrogen?
Problem 2
True or False: Most of the net primary productivity that is consumed is used for growth by primary consumers. Explain.
Problem 3
Which of the following is the longest-lived reservoir for carbon?
a. Atmospheric CO2
b. Marine plankton (primary producers and consumers)
c. Fossil fuels
d. Wood
Problem 4
In a model of the carbon cycle, how would you label an arrow from the atmosphere to plants?
a. cellular respiration
b. photosynthesis
c. decomposition
d. consumption
Problem 5
If the GPP of a grassland is 5000 kcal/m2/year and 55 percent is used up by cellular respiration, what is the NPP?
a. 2250 kcal/m2/year
b. 2750 kcal/m2/year
c. 5000 kcal/m2/year
d. Need more data
Problem 6
Explain why decomposition rates in a field in Nebraska would differ from the decomposition rates in a field in the Amazon. How do decomposers regulate nutrient availability in ecosystems?
Problem 7
Why are the open oceans nutrient poor? Why are coastal areas and intertidal habitats relatively nutrient rich?
Problem 8
Explain why it is more energy efficient (in terms of the amount of total NPP required) to eat a pound of tofu (bean curd) than a pound of hamburger.
Problem 9
Suppose that record snows blanket your campus this winter. Your friend says this is proof that global warming isn't really occurring. What is the flaw in your friend's logic?
a. The average temperature of the Earth is not actually increasing.
b. Global warming refers to temperatures, but snow is a type of precipitation.
c. While the average global temperature is increasing, local temperatures and precipitation (weather) will vary.
d. Your friend is confusing global warming and global climate change.
Problem 10
During the Carboniferous period, plant growth was extensive but rates of decomposition slowed (probably due to the formation of vast, oxygen-poor swamp habitats). As a result, large amounts of biomass accumulated in terrestrial environments (much of this biomass is now coal). The fossil record indicates that atmospheric oxygen increased, atmospheric carbon dioxide decreased, and global temperatures dropped. Explain why.
Problem 11
Scientists around the world are collaborating to understand how deforestation, climate change, and natural processes will interact to affect one of the most productive and biodiverse ecosystems on Earth.
Which of the following biomes typically has the highest net primary productivity?
a. Temperate forest
b. Tropical dry forest
c. Tropical grassland
d. Tropical wet forest
Problem 12
Scientists around the world are collaborating to understand how deforestation, climate change, and natural processes will interact to affect one of the most productive and biodiverse ecosystems on Earth.
Select True or False for each statement about the effects of clear-cutting on the Amazon rain forest, then explain your reasoning.
T/F Nutrient export is likely to decline.
T/F Atmospheric CO2 is likely to decline.
T/F Soil moisture is likely to decline.
T/F Species diversity is likely to decline.
Problem 13
Scientists around the world are collaborating to understand how deforestation, climate change, and natural processes will interact to affect one of the most productive and biodiverse ecosystems on Earth.
Researchers have measured the effects of periodic forest fires on primary productivity in Amazon rain forest plots, comparing years with average precipitation and years with severe drought. Propose which controls would be necessary for such studies.
Problem 14
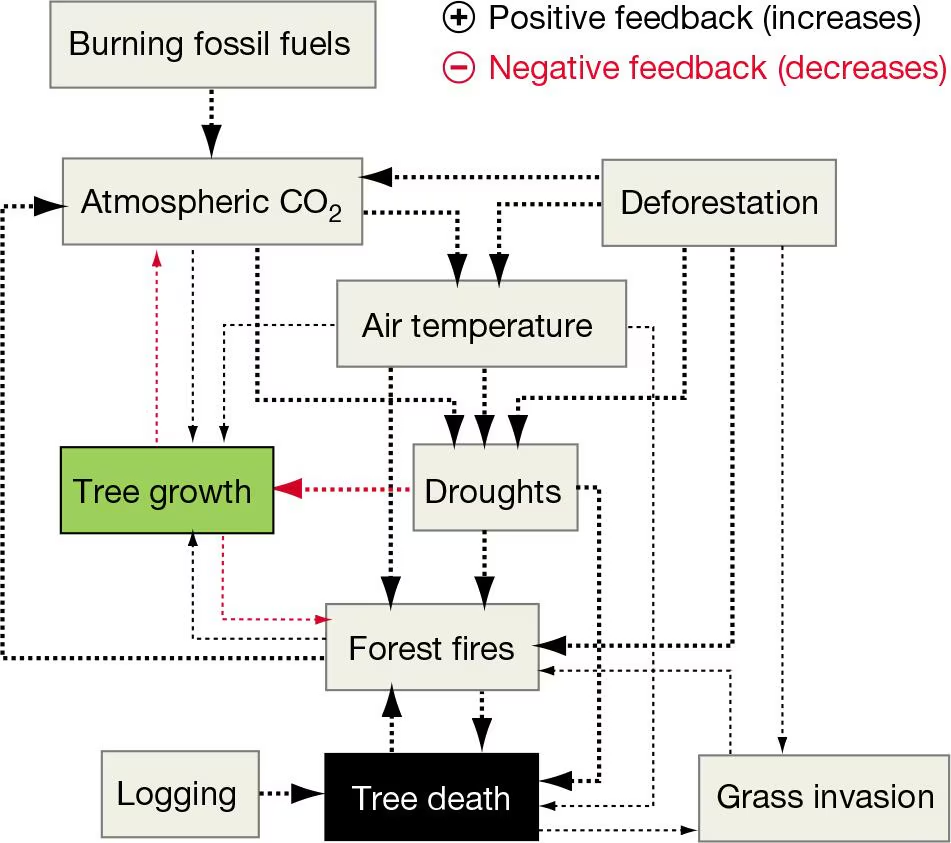
Scientists around the world are collaborating to understand how deforestation, climate change, and natural processes will interact to affect one of the most productive and biodiverse ecosystems on Earth.
This box-and-arrow model summarizes some of the feedback links observed in the Amazon rain forest. Select True or False for the statements that follow, based on whether they are represented by the model. (Note that the boxes and arrows in this model are used differently than those in the nutrient cycle models).

T/F The burning of fossil fuels increases atmospheric CO2.
T/F Tree growth reduces atmospheric CO2.
T/F The death of trees promotes the invasion of grasses.
T/F An increase in CO2 increases the frequency of droughts.
T/F Drought increases the frequency of forest fires.
Problem 15
Scientists around the world are collaborating to understand how deforestation, climate change, and natural processes will interact to affect one of the most productive and biodiverse ecosystems on Earth.
Many studies have raised the concern that positive feedback loops among numerous variables in the Amazon will cause an ecosystem tipping point—a rapid and irreversible transition from forest to grassland. Use the model in Question 14 as a tool to summarize a possible sequence of effects that could cause a transition from forest to grassland.
Problem 16
Researchers use models like the business-as-usual model to examine the possible effects of climate change on both terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems. These models are not predictions of our future, but instead allow us to make decisions now to avoid future problems. Provide examples of how society should change to reduce the impact of climate change on our oceans.
Problem 16f
Scientists around the world are collaborating to understand how deforestation, climate change, and natural processes will interact to affect one of the most productive and biodiverse ecosystems on Earth. Journalists must be concise when reporting science news. Why might journalists and the public struggle to understand and discuss ecosystems ecology and global warming?