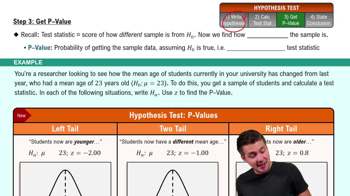
Testing Hypotheses
In Exercises 13–24, assume that a simple random sample has been selected and test the given claim. Unless specified by your instructor, use either the P-value method or the critical value method for testing hypotheses. Identify the null and alternative hypotheses, test statistic, P-value (or range of P-values), or critical value(s), and state the final conclusion that addresses the original claim.
Systolic Blood Pressure Systolic blood pressure levels above 120 mm Hg are considered to be high. For the 300 systolic blood pressure levels listed in Data Set 1 “Body Data” from Appendix B, the mean is 122.96000 mm Hg and the standard deviation is 15.85169 mm Hg. Use a 0.01 significance level to test the claim that the sample is from a population with a mean greater than 120 mm Hg.