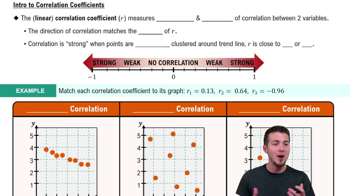
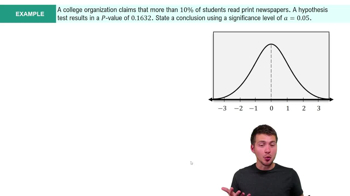
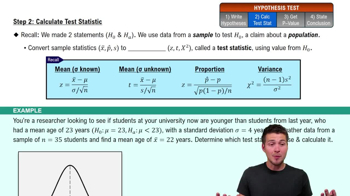
Rank Sums Exercise 12 uses Data Set 33 “Disney World Wait Times” in Appendix B, and the sample size for the 5:00 PM Tower of Terror wait times is n = 50.
c. If we have sample paired data with 50 nonzero differences and the sum of the positive ranks is 165, find the absolute value of the sum of the negative ranks.