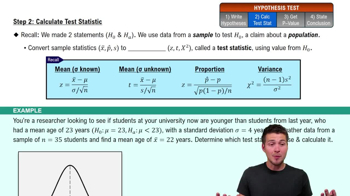
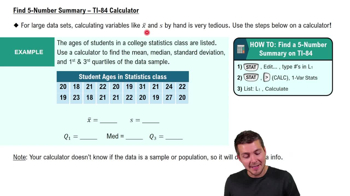
Exercises 1–10 are based on the following sample data consisting of costs of dinner (dollars) and the amounts of tips (dollars) left by diners. The data were collected by students of the author.
[IMAGE]
Fixed Percentage If a restaurant were to change its tipping policy so that a constant tip of 20% of the bill is added to the cost of the dinner, what would be the value of the linear correlation coefficient for the paired amounts of dinners/tips?