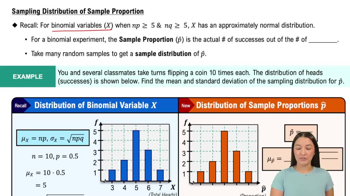
Can Dogs Detect Malaria? A study was conducted to determine whether dogs could detect malaria from socks worn by malaria patients and socks worn by patients without malaria. Among 175 socks worn by malaria patients, the dogs made correct identifications 123 times. Among 145 socks worn by patients without malaria, the dogs made correct identifications 131 times (based on data presented at an annual meeting of the American Society of Tropical Medicine, by principal investigator Steve Lindsay). Use a 0.05 significance level to test the claim of no difference between the two rates of correct responses.
c. What do the results suggest about the use of dogs to detect malaria?