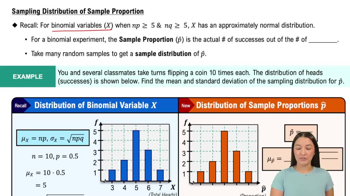
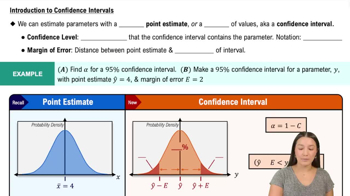
A company wants to test the effectiveness of a new acne cream. The company recruits 500 girls ages 13 to 17 who have acne. The subjects are randomly assigned into two groups. One group is given the acne cream and the other is given a placebo that looks exactly like the acne cream. Both groups apply the cream daily for two months. Facial photos are taken at the beginning and end of the treatment to compare results.
b. Identify a potential problem with the experimental design being used and suggest a way to improve it.