In Exercises 5–8, use (a) randomization and (b) bootstrapping for the indicated exercise from Section 9-1. Compare the results to those obtained in the original exercise.
Exercise 9 in Section 9-1 “Cell Phones and Handedness”

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: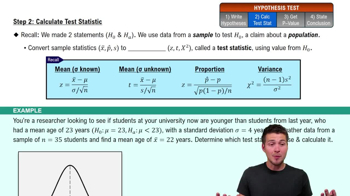


 6:21m
6:21mMaster Step 1: Write Hypotheses with a bite sized video explanation from Patrick
Start learning