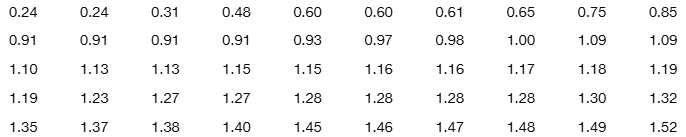
Comparing Values. In Exercises 13–16, use z scores to compare the given values.
Tallest and Shortest Men The tallest adult male was Robert Wadlow, and his height was 272 cm. The shortest adult male was Chandra Bahadur Dangi, and his height was 54.6 cm. Heights of men have a mean of 174.12 cm and a standard deviation of 7.10 cm. Which of these two men has the height that is more extreme?