Finding the Equation of the Regression Line
In Exercises 9 and 10, use the given data to find the equation of the regression line. Examine the scatterplot and identify a characteristic of the data that is ignored by the regression line.
[IMAGE]
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: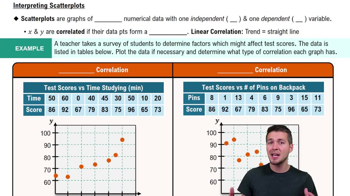

 2:13m
2:13mMaster Introduction to Statistics Channel with a bite sized video explanation from Patrick
Start learning