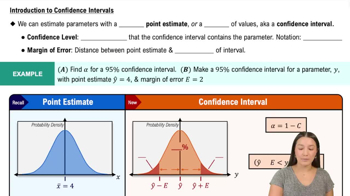
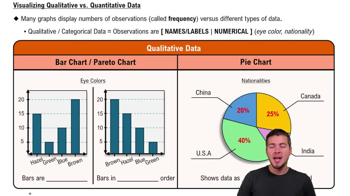
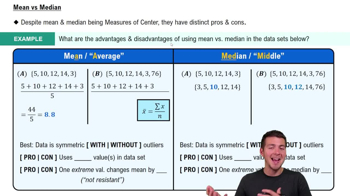
Mean Pulse Rate of Males Data Set 1 “Body Data” in Appendix B includes pulse rates of 153 randomly selected adult males, and those pulse rates vary from a low of 40 bpm to a high of 104 bpm. Find the minimum sample size required to estimate the mean pulse rate of adult males. Assume that we want 99% confidence that the sample mean is within 2 bpm of the population mean.
a. Find the sample size using the range rule of thumb to estimate .