Identify the sampling technique used, and discuss potential sources of bias (if any). Explain.
A student asks 18 friends to participate in a psychology experiment.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: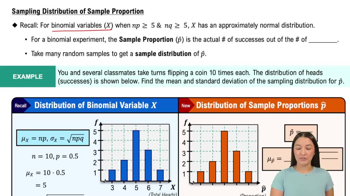

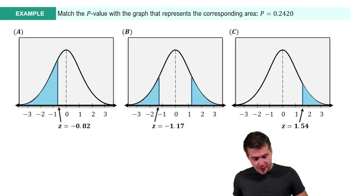

 2:13m
2:13mMaster Introduction to Statistics Channel with a bite sized video explanation from Patrick
Start learning