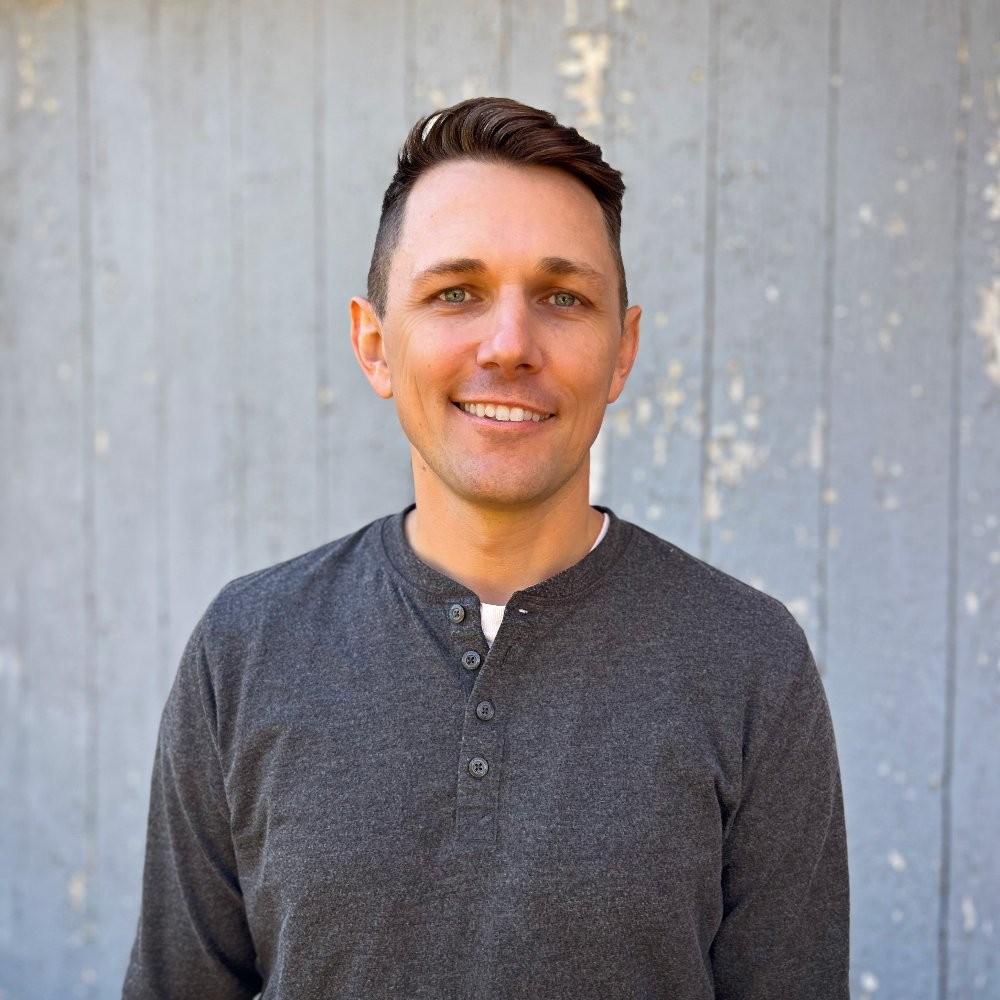
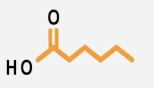
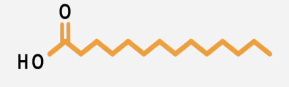
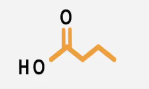
Fatty acids are essential components of dietary lipids, including triglycerides and phospholipids, consisting of hydrocarbon chains made up of carbon and hydrogen atoms, with a carboxylic acid group (-COOH) at one end. The properties of fatty acids significantly influence their health effects when consumed. Key properties include:
1. Fatty Acid Length: Fatty acids can vary in length, with some being longer and others shorter. This length can affect how the body metabolizes these acids.
2. Hydrogen Saturation: Fatty acids can be classified based on their saturation with hydrogen. Saturated fatty acids contain the maximum number of hydrogen atoms, while unsaturated fatty acids have fewer due to the presence of double bonds. This distinction is crucial as it influences the physical state of the fatty acids at room temperature and their health implications.
3. Configuration: The three-dimensional arrangement of atoms in fatty acids, particularly those with double bonds, can vary even among fatty acids of the same length and saturation. This configuration can affect how the body processes these fatty acids and their overall health impact.
Understanding these properties will be essential as we delve deeper into the role of fatty acids in nutrition and health.