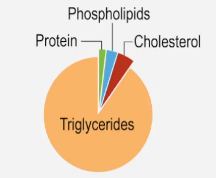
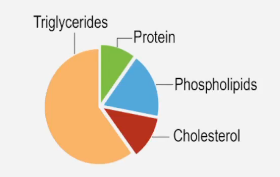
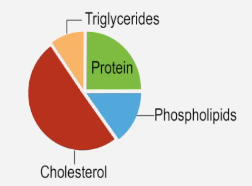
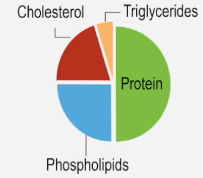
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a broad term that encompasses various conditions affecting the heart and blood vessels. It includes serious disorders such as coronary artery disease, stroke, and heart failure. Alarmingly, CVD is the leading cause of death globally, accounting for over 30% of deaths in the United States alone.
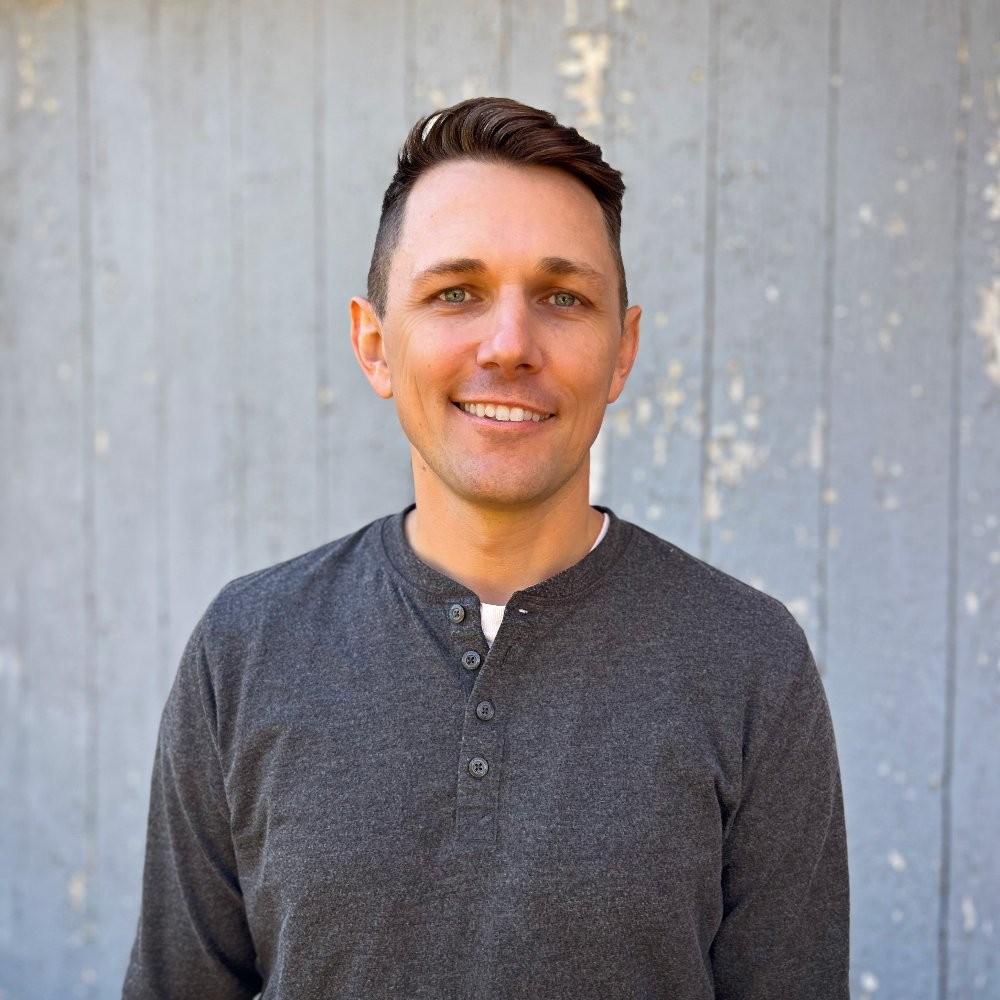
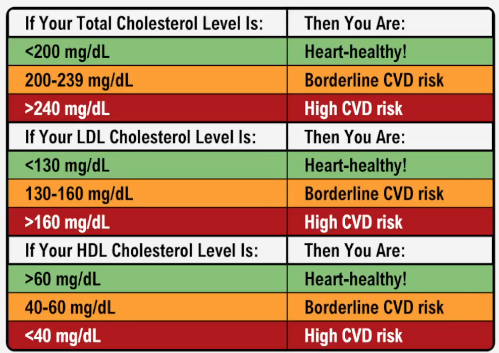
Two primary risk factors contribute significantly to the development of cardiovascular diseases: atherosclerosis and hypertension. Atherosclerosis is characterized by the accumulation of fatty plaques in the arteries, which narrows and hardens them, thereby impeding blood flow to vital tissues. In contrast, hypertension, or high blood pressure, increases the likelihood of developing health complications, including cardiovascular diseases.
Additional risk factors for CVD include obesity, smoking, poor diet, excessive alcohol consumption, age, genetics, and stress. While some of these factors, like diet and exercise, can be managed through lifestyle changes, others, such as age and genetic predisposition, are beyond individual control. Understanding these risk factors is crucial for prevention and management of cardiovascular diseases.