Back
BackProblem 1
Which of the following does not kill endospores?
a. Autoclaving
b. Incineration
c. Hot-air sterilization
d. Pasteurization
e. All of the above kill endospores
Problem 1
The thermal death time for a suspension of Bacillus subtilis endospores is in dry heat and less than in an autoclave. Which type of heat is more effective? Why?
Problem 2
If pasteurization does not achieve sterilization, why is pasteurization used to treat food?
Problem 2
Which of the following is most effective for sterilizing mattresses and plastic Petri dishes?
a. Chlorine
b. Ethylene oxide
c. Glutaraldehyde
d. Autoclaving
e. Nonionizing radiation
Problem 3
Thermal death point is not considered an accurate measure of the effectiveness of heat sterilization. List three factors that can alter thermal death point.
Problem 3
Which of these disinfectants does not act by disrupting the plasma membrane?
a. Phenolics
b. Phenol
c. Quats
d. Halogens
e. Biguanides
Problem 4
Which of the following cannot be used to sterilize a heat-labile solution stored in a plastic container?
a. Gamma radiation
b. Ethylene oxide
c. Supercritical fluids
d. Autoclaving
e. Short-wavelength radiation
Problem 4
The antimicrobial effect of gamma radiation is due to:(a) ________.
The antimicrobial effect of ultraviolet radiation is due to: (b) ________.
Problem 5
Which of the following is used to control microbial growth in foods?
a. Organic acids
b. Alcohols
c. Aldehydes
d. Heavy metals
e. All of the above
Problem 5
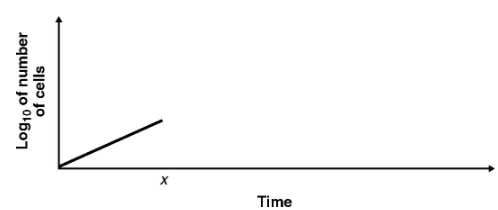
A bacterial culture was in log phase in the following figure. At time x, an antibacterial compound was added to the culture. Draw the lines indicating the addition of a bactericidal compound and a bacteriostatic compound. Explain why the viable count does not immediately drop to zero at x.
Problem 6
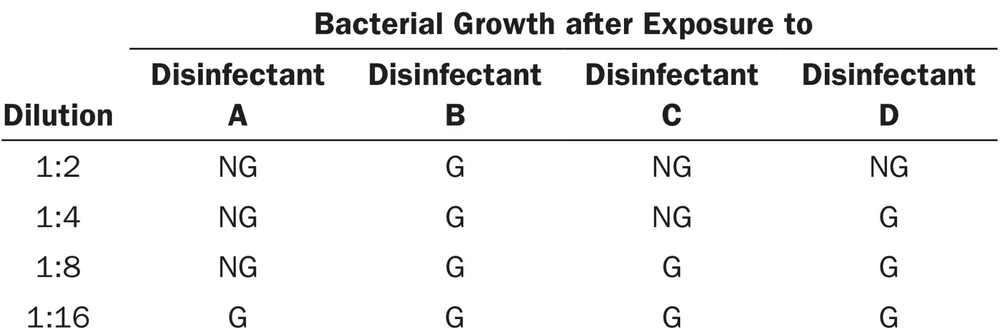
Use the following information to answer questions 6 and 7. The data were obtained from a use-dilution test comparing four disinfectants against Salmonella Choleraesuis.
G = growth, NG = no growth
Which disinfectant is the most effective?
Problem 6
How do autoclaving, hot air, and ultra-high-temperature pasteurization illustrate the concept of equivalent treatments?
Problem 7
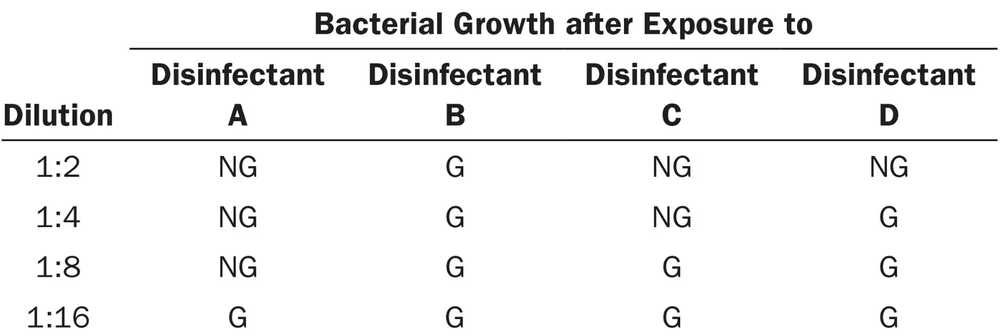
Use the following information to answer questions 6 and 7. The data were obtained from a use-dilution test comparing four disinfectants against Salmonella Choleraesuis.
G = growth, NG = no growth
Which disinfectant(s) is (are) bactericidal?
a. A,B,C, and D
b. A,C, and D
c. A only
d. B only
e. None of the above
Problem 7
How do salts and sugars preserve foods? Why are these considered physical rather than chemical methods of microbial control? Name one food that is preserved with sugar and one preserved with salt. How do you account for the occasional growth of Penicillium mold in jelly, which is 50% sucrose?
Problem 8
Which of the following is not a characteristic of quaternary ammonium compounds?
a. Bactericidal against gram-positive bacteria
b. Sporicidal
c. Amebicidal
d. Fungicidal
e. Kills enveloped viruses
Problem 8
The use-dilution values for two disinfectants tested under the same conditions are as follows:
Disinfectant A—1:2
Disinfectant B—1:10,000.
If both disinfectants are designed for the same purpose, which would you select?
Problem 9
A large hospital washes burn patients in a stainless steel tub. After each patient, the tub is cleaned with a quat. It was noticed that 14 of 20 burn patients acquired Pseudomonas infections after being bathed. Provide an explanation for this high rate of infection.
Problem 9
You and your classmates are trying to determine how a disinfectant might kill cells. You observe that when you spill the disinfectant in a tube of reduced litmus milk, the litmus turns blue again. You suggest to your classmates that:
a. The disinfectant might inhibit cell wall synthesis
b. The disinfectant might oxidize molecules
c. The disinfectant might inhibit protein synthesis
d. The disinfectant might denature proteins
e. The disinfectant might damage DNA
Problem 10
Which of the following is most likely to be bactericidal?
a. Membrane filtration
b. Ionizing radiation
c. Lyophilization (freeze-drying)
d. Deep-freezing
e. All of the above
Problem 10
What bacteria have porins, are resistant to bisphenols, and survive and may grow in quats?