Back
BackProblem 1
Briefly describe the components of DNA, and explain its functional relationship to RNA and protein.
Problem 1
Transfer of DNA from a donor to a recipient cell by a bacteriophage.
a. Conjugation
b. Transcription
c. Transduction
d. Transformation
e. Translation
Problem 2
Transfer of DNA from a donor to a recipient as naked DNA in solution.
a. Conjugation
b. Transcription
c. Transduction
d. Transformation
e. Translation
Problem 2
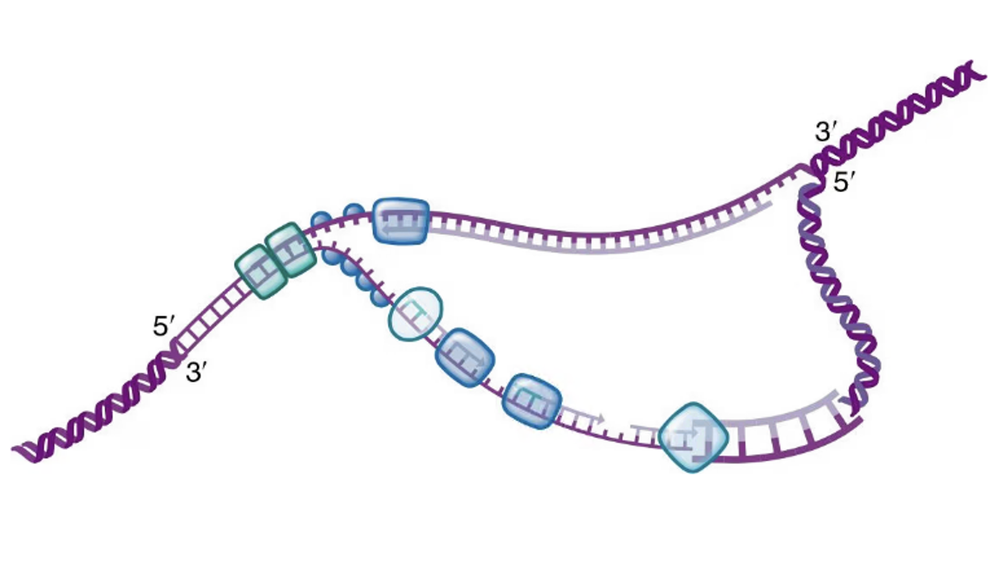
Identify and mark each of the following on the portion of DNA undergoing replication: replication fork, DNA polymerase, RNA primer, parent strands, leading strand, lagging strand, the direction of replication on each strand, and the 5′ end of each strand.
Problem 3
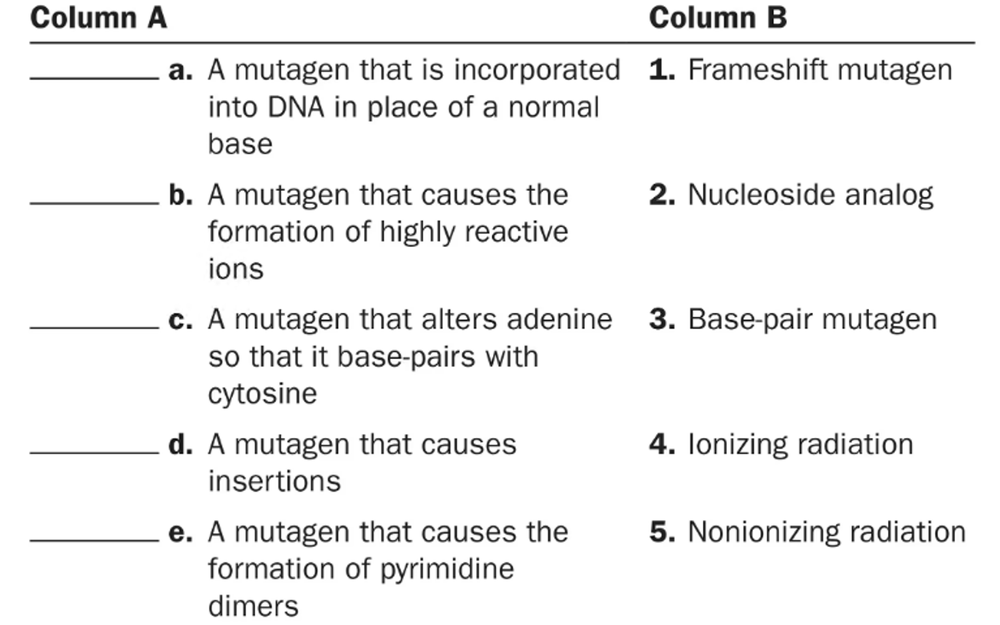
Match the following examples of mutagens.
Problem 3
Feedback inhibition differs from repression because feedback inhibition
a. Is less precise.
b. Is slower acting.
c. Stops the action of preexisting enzymes.
d. Stops the synthesis of new enzymes.
e. All of the above
Problem 4
Bacteria can acquire antibiotic resistance by all of the following except
a. mutation.
b. insertion of transposons.
c. conjugation.
d. snRNPs.
e. transformation.
Problem 4
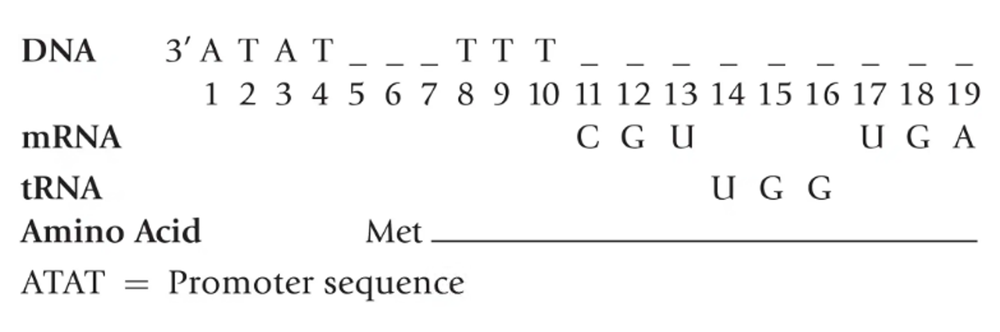
The following is a code for a strand of DNA.
a. Using the genetic code provided in Figure 8.8, fill in the blanks to complete the segment of DNA shown.
b. Fill in the blanks to complete the sequence of amino acids coded for by this strand of DNA.
c. Write the code for the complementary strand of DNA completed in part (a).
d. What would be the effect if C were substituted for T at base 10?
e. What would be the effect if A were substituted for G at base 11?
f. What would be the effect if G were substituted for T at base 14?
g. What would be the effect if C were inserted between bases 9 and 10?
h. How would UV radiation affect this strand of DNA?
i. Identify a nonsense sequence in this strand of DNA.
Problem 5
Suppose you inoculate three flasks of minimal salts broth with E. coli. Flask A contains glucose. Flask B contains glucose and lactose. Flask C contains lactose. After a few hours of incubation, you test the flasks for the presence of ß-galactosidase. Which flask(s) do you predict will have this enzyme?
a. A
b. B
c. C
d. A and B
e. B and C
Problem 6
Plasmids differ from transposons in that plasmids
a. become inserted into chromosomes.
b. are self-replicated outside the chromosome.
c. move from chromosome to chromosome.
d. carry genes for antibiotic resistance.
e. none of the above
Problem 6
Identify when (before transcription, after transcription but before translation, after translation) each of the following regulatory mechanisms functions.
a. ATP combines with an enzyme, altering its shape.
b. A short RNA is synthesized that is complementary to mRNA.
c. Methylation of DNA occurs.
d. An inducer combines with a repressor.
Problem 7
Which sequence is the best target for damage by UV radiation: AGGCAA, CTTTGA, or GUAAAU? Why aren’t all bacteria killed when they are exposed to sunlight?
Problem 7
Use the following choices to answer the question:
a. Catabolite repression
b. DNA polymerase
c. Induction
d. Repression
e. Translation
Mechanism by which the presence of glucose inhibits the lac operon.
Problem 8
Use the following choices to answer the question:
a. Catabolite repression
b. DNA polymerase
c. Induction
d. Repression
e. Translation
The mechanism by which lactose controls the lac operon.
Problem 8
You are provided with cultures with the following characteristics:
Culture 1: F+, genotype A+B+C+
Culture 2: F ̄, genotype A ̄B ̄C ̄
a. Indicate the possible genotypes of a recombinant cell resulting from the conjugation of cultures 1 and 2.
b. Indicate the possible genotypes of a recombinant cell resulting from conjugation of the two cultures after the F+ has become an Hfr cell.
Problem 9
Two offspring cells are most likely to inherit which one of the following from the parent cell?
a. A change in a nucleotide in mRNA
b. A change in a nucleotide in tRNA
c. A change in a nucleotide in rRNA
d. A change in a nucleotide in DNA
e. A change in a protein
Problem 9
Why are mutation and recombination important in the process of natural selection and the evolution of organisms?
Problem 10
Which of the following is not a method of horizontal gene transfer?
a. Binary fission
b. Conjugation
c. Integration of a transposon
d. Transduction
e. Transformation
Problem 10
Normally a commensal in the human intestine, this bacterium became pathogenic after acquiring a toxin gene from a Shigella bacterium.