Back
BackProblem 1
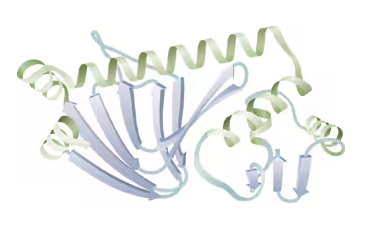
In the following molecule, label a portion that shows only primary structure; label two types of secondary structure; circle the tertiary structure.
Problem 1
The outermost electron shell of an atom is known as the _____________ shell.
Problem 1
Which of the following structures have no electrical charge?
a. Protons
b. Electrons
c. Neutrons
d. Ions
Problem 1
List three main types of chemical bonds, and give an example of each.
Problem 2
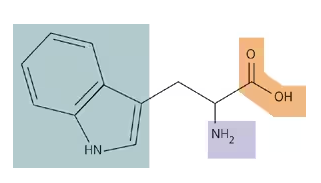
Shown is the amino acid tryptophan. Put the letter “C” at the site of every carbon atom. Label the amino group, the carboxyl group, and the side group.
Problem 2
The type of chemical bond between atoms with nearly equal electronegativities is called a(n) _____________ bond.
Problem 2
The atomic mass of an atom most closely approximates the sum of the masses of all its __________.
a. protons
b. isotopes
c. electrons
d protons and neutrons
Problem 2
Name five properties of water that are vital to life.
Problem 3
The principal short-term energy storage molecule in cells is __________ .
Problem 3
Describe the difference(s) among saturated fatty acids, unsaturated fatty acids, and polyunsaturated fatty acids.
Problem 3
One isotope of iodine differs from another in __________ .
a. the number of protons
b. the number of electrons
c. the number of neutrons
d. atomic number
Problem 4
Common long-term energy storage molecules are __________ , __________ , __________ , and __________.
Problem 4
What is the difference between atomic oxygen and molecular oxygen?
Problem 4
Which of the following is not an organic compound?
a. Monosaccharide
b. Formaldehyde
c. Water
d. Steroid
Problem 5
Groups of atoms such as NH₂ or OH that appear in certain common arrangements are called __________ .
Problem 5
Explain how the polarity of water molecules makes water an excellent solvent.
Problem 5
Which of the following terms most correctly describes the bonds in a molecule of water?
a. Nonpolar covalent bond
b. Polar covalent bond
c. Ionic bond
d. Hydrogen bond
Problem 6
In water, cations and anions of salts dissociate from one another and become surrounded by water molecules. In this state, the ions are also called __________ .
a. electrically negative
b. ionically bonded
c. electrolytes
d. hydrogen bonds
Problem 6
The reverse of dehydration synthesis is __________ .
Problem 7
Which of the following can be most accurately described as a decomposition reaction?
a. C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6 O₂ → 6 H₂O + 6 CO₂
b. glucose + ATP → glucose phosphate + ADP
c. 6 H₂O + 6 CO₂ → C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6 O₂
d. A + BC → AB + C
Problem 7
Reactions that release energy are called __________ reactions.
Problem 8
All chemical reactions begin with reactants and result in new molecules called __________ .
Problem 8
Which of the following statements about a carbonated cola beverage with a pH of 2.9 is true?
a. It has a relatively high concentration of hydrogen ions.
b. It has a relatively low concentration of hydrogen ions.
c. It has equal amounts of hydroxyl and hydrogen ions.
d. Cola is a buffered solution.
Problem 9
The __________ scale is a measure of the concentration of hydrogen ions in a solution.
Problem 9
Proteins are polymers of __________.
a. Amino acids
b. Fatty acids
c. Nucleic acids
d. Monosaccharides
Problem 10
A nucleic acid containing the base uracil would also contain __________ sugar.
Problem 10
Which of the following are hydrophobic organic molecules?
a. Proteins
b. Carbohydrates
c. Lipids
d. Nucleic acids
Problem 18
In DNA, adenine forms ___________ hydrogen bonds with ____________.
a. Three / uracil
b. Two / uracil
c. Two / thymine
d. Three / thymine