Back
BackProblem 1
A cell may allow a large or charged chemical to move across the cytoplasmic membrane, down the chemical’s electrical and chemical gradients, in a process called _________ . .
a. active transport
b. facilitated diffusion
c. endocytosis
d. pinocytosis
Problem 1
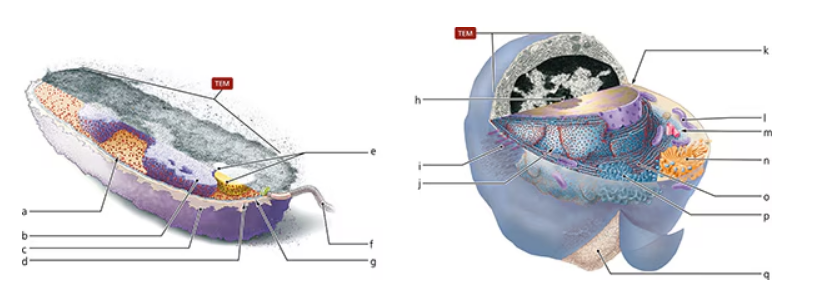
Label the structures of the following prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. With a single word or short phrase, explain the function of each structure.
a.
b.
c.
d.
e.
f.
g.
h.
i.
j.
k.
l.
m.
n.
o.
p.
q.
Problem 1
Describe (or draw) an example of diffusion down a concentration gradient.
Problem 1
Match the structures with their descriptions following. A letter may be used more than once or not at all, and more than one letter may be correct for each blank.
____ Glycocalyx
____ Flagella
____ Axial filaments
____ Cilia
____ Fimbriae
____ Pili
____ Hami
A. Bristlelike projections found in quantities of 100 or more
B. Long whip
C. Responsible for conjugation
D. “Sweet cup” composed of polysaccharides and/or polypeptides
E. Numerous “grappling-hook” projections
F. Responsible for motility of spirochetes
G. Extensions not used for cell motility
H. Made of tubulin in eukaryotes
I. Made of flagellin in bacteria
Problem 2
Label each type of flagellar arrangement.
a. __________ <IMAGE> b. __________ <IMAGE>
c. __________ <IMAGE> d. __________ <IMAGE>
Problem 2
Match the terms with their descriptions following. Only one description is intended for each term.
____ Ribosome
____ Cytoskeleton
____ Centriole
____ Nucleus
____ Mitochondrion
____ Chloroplast
____ ER
____ Golgi body
____ Peroxisome
A. Site of protein synthesis
B. Contains enzymes to neutralize hydrogen peroxide
C. Functions as the transport system within a eukaryotic cell
D. Allows contraction of the cell
E. Site of most DNA in eukaryotes
F. Contains microtubules in "9 + 0" arrangement
G. Light-harvesting organelle
H. Packages large molecules for export from a cell
I. Its internal membranes are sites for ATP production
Problem 2
Sketch, name, and describe three flagellar arrangements in bacteria.
Problem 2
Which of the following statements concerning growth and reproduction is false?
a. Growth and reproduction may occur simultaneously in living organisms
b. A living organism must reproduce to be considered alive
c. Living things may stop growing and reproducing yet still be alive
d. Normally, living organisms have the ability to grow and reproduce themselves
Problem 3
Define cytosol.
Problem 3
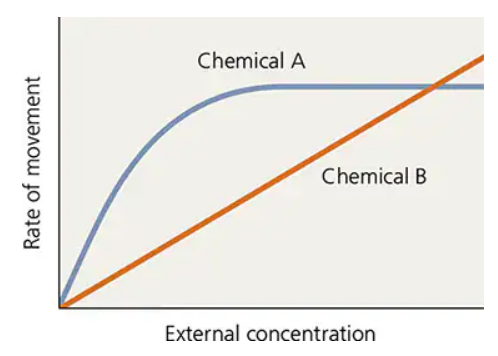
A scientist who is studying passive movement of chemicals across the cytoplasmic membrane of Salmonella enterica serotype Typhi measures the rate at which two chemicals diffuse into a cell as a function of external concentration. The results are shown in the following figure. Chemical A diffuses into the cell more rapidly than does B at lower external concentrations, but the rate levels off as the external concentration increases. The rate of diffusion of chemical B continues to increase as the external concentration increases.
a. How can you explain the differences in the diffusion rates of chemicals A and B?
b. Why does the diffusion rate of chemical A taper off?
c. How could the cell increase the diffusion rate of chemical A?
d. How could the cell increase the diffusion rate of chemical B?
Problem 3
A "9 + 2" arrangement of microtubules is seen in __________ .
a. archaeal flagella
b. bacterial flagella
c. eukaryotic flagella
d. all prokaryotic flagella
Problem 3.8a
Which of the following is not a function of a glycocalyx?
a. It forms pseudopods for faster mobility of an organism.
b. It can protect a bacterial cell from drying out.
c. It hides a bacterial cell from other cells.
d. It allows a bacterium to stick to a host.
Problem 4
The term fluid mosaic has been used in describing the cytoplasmic membrane. How does each word of that phrase accurately describe our current understanding of a cell membrane?
Problem 4
Which of the following is most associated with diffusion?
a. Symports
b. Antiports
c. Carrier proteins
d. Endocytosis
Problem 5
Which of the following is not associated with prokaryotic organisms?
a. Nucleoid
b. Glycocalyx
c. Cilia
d. Circular DNA
Problem 5
A local newspaper writer has contacted you, an educated microbiology student from a respected college. He wants to obtain scientific information for an article he is writing about “life” and poses the following query: “What is the difference between a living thing and a nonliving thing?” Knowing that he will edit your material to fit the article, give an intelligent, scientific response.
Problem 6
What is the difference between growth and reproduction?
Problem 6
Which of the following is true of Svedbergs?
a. They are not exact but are useful for comparisons.
b. They are abbreviated “sv.”
c. They are prokaryotic in nature but exhibit some eukaryotic characteristics.
d. They are an expression of sedimentation rate during high-speed centrifugation.
Problem 7
Compare bacterial cells and algal cells, giving at least four similarities and four differences.
Problem 7
Which of the following statements is true?
a. The cell walls of bacteria are composed of peptidoglycan.
b. Peptidoglycan is a fatty acid.
c. Gram-positive bacterial walls have a relatively thin layer of peptidoglycan anchored to the cytoplasmic membrane by teichoic acids.
d. Peptidoglycan is found mainly in the cell walls of fungi, algae, and plants.
Problem 8
Contrast a cell of Streptococcus pyogenes (a bacterium) with the unicellular protozoan Entamoeba histolytica, listing at least eight differences.
Problem 8
Which of the following is not a function of a glycocalyx?
a. It forms pseudopods for faster mobility of an organism.
b. It can protect a bacterial cell from drying out.
c. It hides a bacterial cell from other cells.
d. It allows a bacterium to stick to a host.
Problem 9
Differentiate among pili, fimbriae, and cilia, using sketches and descriptive labels.
Problem 9
Bacterial flagella are __________ .
a. anchored to the cell by a basal body
b. composed of hami
c. surrounded by an extension of the cytoplasmic membrane
d. composed of tubulin in hollow microtubules in a "9 + 2" arrangement
Problem 10
Which cellular structure is important in classifying a bacterial species as Gram positive or Gram negative?
a. Flagella
b. Cell wall
c. Cilia
d. Glycocalyx
Problem 10
Can nonliving things metabolize? Explain your answer.
Problem 11
How do archaeal flagella differ from bacterial flagella and eukaryotic flagella?
Problem 11
A Gram-negative cell is moving uric acid across the cytoplasmic membrane against its chemical gradient. Which of the following statements is true?
a. The exterior of the cell is probably electrically negative compared to the interior of the cell.
b. The acid probably moves by a passive means such as facilitated diffusion.
c. The acid moves by an active process such as active transport.
d. The movement of the acid requires phagocytosis.
Problem 12
Gram-positive bacteria __________.
a. have a thick cell wall, which retains crystal violet dye
b. contain teichoic acids in their cell walls
c. appear purple after Gram staining
d. all of the above
Problem 12
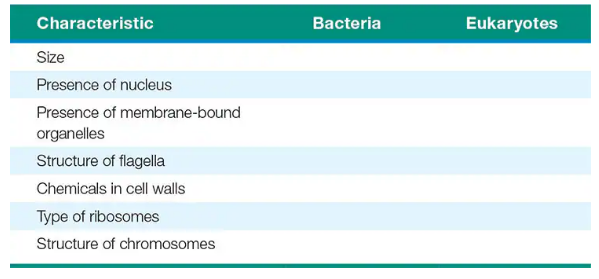
Contrast bacterial and eukaryotic cells by filling in the following table.