Textbook Question
What metabolic substrate(s) are produced from the carbon atoms of each of the following amino acids?
b. asparagine
1
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
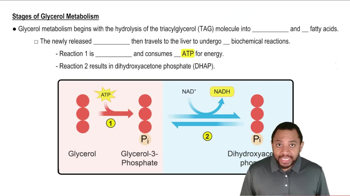
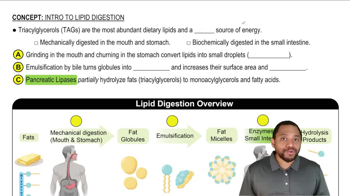
What metabolic substrate(s) are produced from the carbon atoms of each of the following amino acids?
b. asparagine
Arachidic acid is a C20 fatty acid found in peanut and fish oils.
a. How many cycles of β oxidation are needed for the complete oxidation of arachidic acid?
Arachidic acid is a C20 fatty acid found in peanut and fish oils.
c. Calculate the total ATP yield from the complete β oxidation of arachidic acid by completing the following:
Identify the type of food as carbohydrate, fat, or protein that gives each of the following digestion products:
e. amino acids
Identify each of the following as a six-carbon or a three-carbon compound and arrange them in the order in which they occur in glycolysis:
a. 3-phosphoglycerate